PostgreSQL vs Microsoft SQL Server: The Ultimate Database Comparison Guide for 2025
Choosing the right database management system can make or break your organization’s data strategy. Two powerhouses dominate the enterprise database landscape: PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQL Server. This comprehensive comparison examines every critical aspect of these database systems to help you make an informed decision that aligns with your technical requirements, budget constraints, and long-term business objectives.
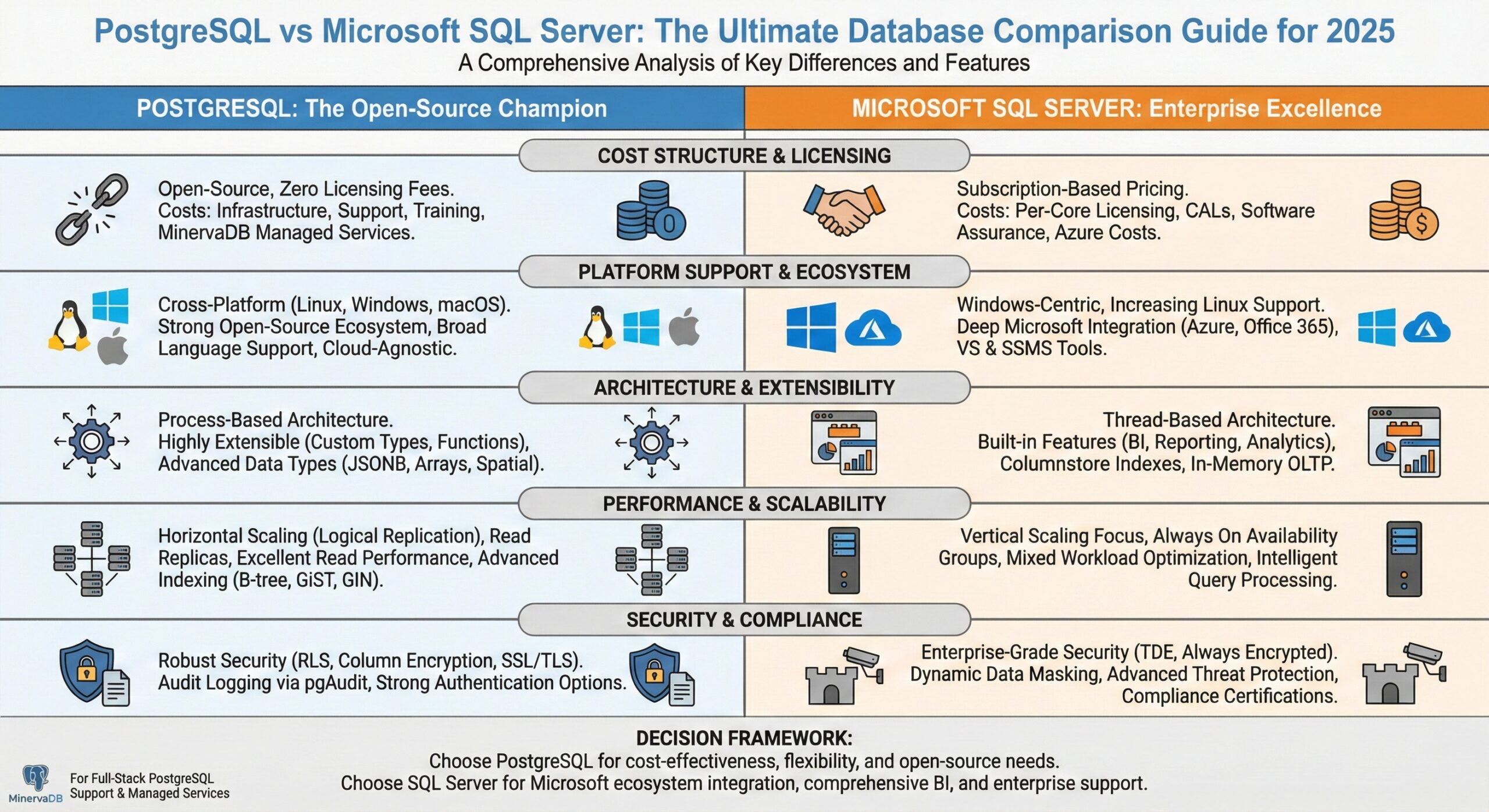
Executive Summary: Key Differences at a Glance
PostgreSQL stands out as an open-source, standards-compliant database system renowned for its extensibility and advanced features. Microsoft SQL Server represents a mature, enterprise-focused solution with deep integration into the Microsoft ecosystem and comprehensive business intelligence capabilities.
Quick Comparison Overview:
- Cost Structure: PostgreSQL offers zero licensing fees vs SQL Server’s subscription-based pricing
- Platform Support: PostgreSQL runs on multiple operating systems vs SQL Server’s Windows-centric approach
- Performance: Both deliver excellent performance with different optimization strengths
- Scalability: PostgreSQL excels in horizontal scaling vs SQL Server’s vertical scaling advantages
- Enterprise Features: SQL Server provides more built-in business tools vs PostgreSQL’s extensible architecture
Understanding PostgreSQL: The Open-Source Database Champion
PostgreSQL has evolved into one of the world’s most sophisticated open-source database systems since its inception in the 1980s. Originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley, it has grown through community contributions into a feature-rich platform that rivals any commercial database solution.
Core Strengths of PostgreSQL:
- Advanced data types including JSON, XML, arrays, and custom types
- Extensible architecture allowing custom functions, operators, and data types
- ACID compliance ensuring data integrity and transaction reliability
- Multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) for high-performance concurrent access
- Standards compliance following SQL standards more closely than most competitors
PostgreSQL’s Technical Architecture
The system employs a process-based architecture where each client connection spawns a separate server process. This design provides excellent isolation between connections and robust fault tolerance, though it requires more memory overhead compared to thread-based systems.
Advanced indexing capabilities include B-tree, Hash, GiST, SP-GiST, GIN, and BRIN indexes, enabling optimal query performance across diverse data types and access patterns. The query planner utilizes sophisticated cost-based optimization to select the most efficient execution plans.
Microsoft SQL Server: Enterprise Database Excellence
Microsoft SQL Server represents decades of enterprise database innovation, first released in 1989 and continuously evolved to meet demanding business requirements. The platform integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s broader technology ecosystem while providing robust standalone capabilities.
Core Strengths of SQL Server:
- Comprehensive business intelligence suite with built-in reporting and analytics
- Advanced security features including transparent data encryption and row-level security
- High availability solutions with Always On availability groups and failover clustering
- Deep Microsoft ecosystem integration with Azure, Office 365, and Windows Server
- Professional support with guaranteed service level agreements
SQL Server’s Technical Architecture
The system utilizes a shared-memory architecture with multiple threads serving client requests within a single process. This approach provides efficient resource utilization and lower memory overhead, particularly beneficial for high-concurrency scenarios.
Intelligent query processing features include adaptive query processing, automatic plan correction, and memory grant feedback, enabling the system to automatically optimize performance based on workload patterns.
Detailed Feature Comparison Analysis
Data Types and Storage Capabilities
PostgreSQL offers superior flexibility in data type support, including:
- Native JSON and JSONB support for document-style data storage
- Array data types for storing multiple values in single columns
- Geometric data types for spatial applications
- Network address types for IP and MAC address storage
- Custom data types through user-defined types and domains
SQL Server provides comprehensive business-focused data types:
- Hierarchical data types for organizational structures
- Spatial data types with advanced geographic capabilities
- XML data type with built-in query and manipulation functions
- Date and time types with timezone awareness
- Large object support through FILESTREAM and FileTable
Performance and Optimization
PostgreSQL Performance Characteristics:
- Excellent read performance through advanced indexing strategies
- Efficient handling of complex queries with sophisticated query planning
- Strong concurrent read performance via MVCC implementation
- Customizable performance tuning through extensive configuration options
- Parallel query execution for improved analytical workload performance
SQL Server Performance Characteristics:
- Optimized for mixed workloads with intelligent resource management
- Advanced caching mechanisms including buffer pool and plan cache optimization
- Columnstore indexes for exceptional analytical query performance
- In-memory OLTP for ultra-high-performance transactional workloads
- Automatic tuning features that adapt to changing workload patterns
Scalability and High Availability
PostgreSQL Scalability Solutions:
- Horizontal scaling through logical replication and partitioning
- Read replicas for distributing read workloads across multiple servers
- Connection pooling solutions like PgBouncer for handling high connection counts
- Streaming replication for real-time data synchronization
- Foreign data wrappers for accessing external data sources
SQL Server Scalability Solutions:
- Always On availability groups for high availability and disaster recovery
- Scale-out solutions through distributed availability groups
- Read-scale availability groups for offloading read workloads
- Failover cluster instances for automatic failover capabilities
- Azure SQL Database for cloud-based elastic scaling
Cost Analysis and Total Ownership Considerations
PostgreSQL Cost Structure
Zero licensing fees represent PostgreSQL’s most significant cost advantage. Organizations only pay for:
- Hardware and infrastructure costs
- Professional services for implementation and optimization
- Staff training and certification programs
- Third-party tools for monitoring and management
- Support contracts: MinervaDB provides full-stack PostgreSQL Consultative Support (24/7) and Managed Services for PostgreSQL, addressing Performance, Scalability, High Availability, and Database Reliability Engineering.
SQL Server Cost Structure
Licensing represents a significant investment for SQL Server deployments:
- Per-core licensing for server installations
- Client Access Licenses (CALs) for user-based licensing models
- Software Assurance for upgrade rights and additional benefits
- Azure SQL Database subscription costs for cloud deployments
- Additional feature licensing for advanced capabilities
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
PostgreSQL typically offers lower total costs for:
- Small to medium-sized deployments with limited budgets
- Development and testing environments requiring multiple instances
- Organizations with strong open-source expertise and internal support capabilities
- Cloud-native applications leveraging managed PostgreSQL services
SQL Server may provide better value for:
- Large enterprise deployments requiring comprehensive support
- Microsoft-centric environments with existing licensing agreements
- Business intelligence-heavy workloads utilizing built-in BI tools
- Mission-critical applications requiring guaranteed support response times
Security and Compliance Capabilities
PostgreSQL Security Features
Robust authentication and authorization mechanisms include:
- Multiple authentication methods including LDAP, Kerberos, and certificate-based authentication
- Row-level security for fine-grained access control
- Column-level encryption for protecting sensitive data
- SSL/TLS encryption for data in transit
- Audit logging through extensions like pgAudit
SQL Server Security Features
Enterprise-grade security capabilities encompass:
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for automatic data-at-rest encryption
- Always Encrypted for client-side encryption with key management
- Dynamic data masking for protecting sensitive information in non-production environments
- Advanced threat protection with anomaly detection and alerting
- Compliance certifications for various industry standards
Development and Integration Ecosystem
PostgreSQL Development Environment
Extensive programming language support includes:
- Native support for SQL, PL/pgSQL, PL/Python, PL/Perl, and PL/Tcl
- Third-party language extensions for Java, R, and other languages
- Rich ecosystem of drivers and ORMs for various programming languages
- Active community providing continuous improvements and extensions
- Cloud provider support with managed services from AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure
SQL Server Development Environment
Comprehensive Microsoft integration features:
- Visual Studio integration with IntelliSense and debugging capabilities
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) for comprehensive database administration
- Integration Services (SSIS) for ETL and data integration workflows
- Reporting Services (SSRS) for enterprise reporting solutions
- Analysis Services (SSAS) for multidimensional data analysis
Performance Benchmarking and Real-World Scenarios
OLTP Workload Performance
PostgreSQL excels in scenarios requiring:
- High concurrent read operations with minimal locking overhead
- Complex analytical queries with advanced indexing strategies
- Mixed workloads combining transactional and analytical processing
- Geographic and spatial data processing with PostGIS extension
SQL Server demonstrates superior performance for:
- Write-heavy workloads with optimized transaction log management
- Business intelligence queries utilizing columnstore indexes
- In-memory processing for ultra-low latency requirements
- Integrated reporting and analytics workloads
Scalability Testing Results
Horizontal scaling advantages favor PostgreSQL in:
- Distributed architectures with multiple database nodes
- Cloud-native deployments requiring elastic scaling capabilities
- Read-heavy workloads distributed across multiple replicas
- Microservices architectures with independent database scaling
Vertical scaling strengths benefit SQL Server in:
- Single-server deployments with high-end hardware configurations
- Consolidated workloads running multiple databases on shared infrastructure
- Enterprise applications requiring predictable performance characteristics
- Legacy system migrations maintaining existing architectural patterns
Migration Strategies and Considerations
Migrating to PostgreSQL
Key migration considerations include:
- Schema conversion from proprietary SQL dialects to PostgreSQL standards
- Application code modifications for database-specific features
- Data type mapping ensuring compatibility across systems
- Performance optimization through proper indexing and configuration
- Staff training on PostgreSQL administration and development practices
Migrating to SQL Server
Migration planning requirements encompass:
- Licensing cost evaluation for the target environment
- Infrastructure assessment for Windows Server requirements
- Integration planning with existing Microsoft technologies
- Feature utilization analysis for built-in business intelligence capabilities
- Support structure establishment for ongoing maintenance and optimization
Industry Use Cases and Success Stories
PostgreSQL Success Scenarios
Organizations choosing PostgreSQL typically benefit from:
- Startups and scale-ups requiring cost-effective, scalable database solutions
- Financial services leveraging advanced data types for complex calculations
- Geographic information systems utilizing PostGIS for spatial data processing
- Web applications requiring JSON document storage and processing
- Research institutions needing extensible platforms for custom data types
SQL Server Success Scenarios
Enterprises selecting SQL Server often require:
- Large corporations with existing Microsoft infrastructure investments
- Business intelligence applications utilizing comprehensive BI toolsets
- Mission-critical systems requiring guaranteed support and service levels
- Compliance-heavy industries benefiting from built-in security and audit features
- Hybrid cloud deployments integrating on-premises and Azure resources
Future Roadmap and Technology Trends
PostgreSQL Evolution
Upcoming developments focus on:
- Enhanced parallel processing capabilities for improved analytical performance
- Advanced partitioning features for better large-scale data management
- Improved JSON and NoSQL functionality for modern application requirements
- Better cloud integration with managed service providers
- Machine learning extensions for in-database analytics capabilities
SQL Server Innovation
Microsoft’s development priorities include:
- Deeper Azure integration for hybrid and cloud-first deployments
- Enhanced AI and machine learning services within the database engine
- Improved Linux support for cross-platform deployments
- Advanced analytics capabilities through integration with Power BI and Azure services
- Container and Kubernetes support for modern application architectures
Making the Right Choice: Decision Framework
Choose PostgreSQL When:
- Budget constraints require minimizing licensing costs
- Open-source philosophy aligns with organizational values
- Extensibility requirements demand custom data types or functions
- Cross-platform deployment spans multiple operating systems
- Development team expertise includes strong open-source database skills
Choose SQL Server When:
- Microsoft ecosystem integration provides significant business value
- Enterprise support requirements mandate guaranteed service levels
- Business intelligence needs require comprehensive built-in BI tools
- Compliance requirements benefit from extensive security certifications
- Legacy system integration depends on Windows-based infrastructure
Conclusion: Strategic Database Selection for Long-Term Success
The choice between PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQL Server ultimately depends on your organization’s specific requirements, technical expertise, budget constraints, and strategic direction. Both platforms offer exceptional capabilities that can support demanding enterprise workloads.
PostgreSQL represents an excellent choice for organizations prioritizing cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and standards compliance. Its open-source nature provides freedom from vendor lock-in while delivering enterprise-grade performance and reliability.
Microsoft SQL Server excels in environments where comprehensive business intelligence, deep Microsoft integration, and enterprise support are critical success factors. The platform’s maturity and extensive feature set make it ideal for large-scale enterprise deployments.
Consider your long-term strategy when making this decision. Evaluate not just current requirements, but also future growth plans, technology trends, and organizational capabilities. Both databases will continue evolving to meet changing market demands, ensuring that either choice can support your organization’s data management needs for years to come.
The most successful database implementations result from thorough evaluation, proper planning, and alignment with business objectives. Whether you choose PostgreSQL’s open-source flexibility or SQL Server’s enterprise integration, focus on building the expertise and infrastructure necessary to maximize your chosen platform’s potential.
Further Reading
- 25 Advanced MySQL DBA Questions and Answers: Master Database Administration
- Generating Numeric Sequences in MySQL: A Comprehensive Guide
- Best Practices for Managing MongoDB Log Files and System Resources
- An Overview of DDL Algorithms in MySQL 8: Enhancing Schema Changes
- MongoDB Wire Protocol: Structure, Evolution, and Advantages
- Comparing OLTP with OLAP