High Task Failures & Data Skew: Mastering Databricks Repartitioning Strategies for Optimal Performance
Introduction: The Hidden Performance Killer in Databricks
In the world of big data processing, data skew represents one of the most common root causes behind slow Spark jobs, leading to high task failures and significant performance degradation in Databricks environments. When working with large-scale distributed systems like Apache Spark on Databricks, one of the most frustrating performance issues you can encounter is prolonged stage execution, often caused by uneven data distribution across partitions.
Data distribution problems don’t just slow down your pipelines—they can bring entire workflows to a grinding halt, causing cascading failures that impact business-critical operations. Understanding and implementing effective repartitioning strategies is essential for maintaining high-performance data engineering workflows.
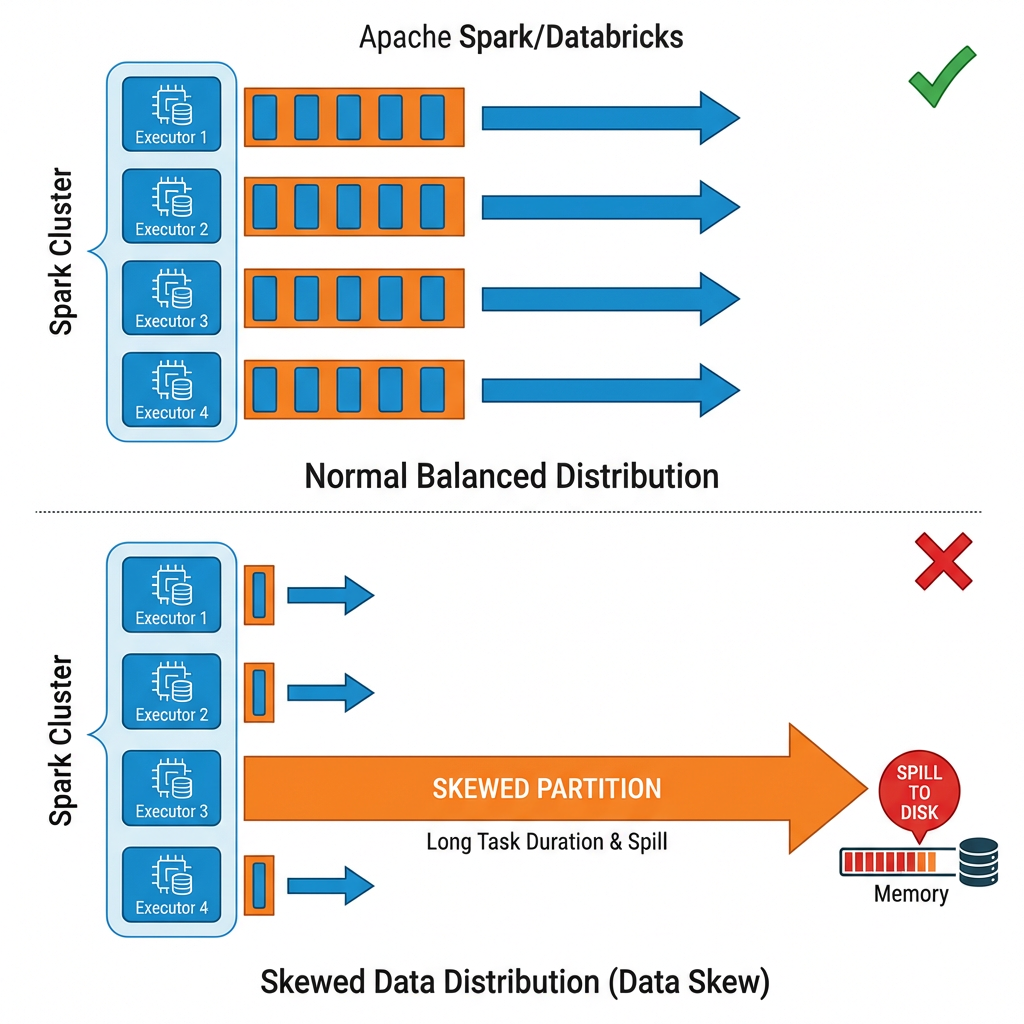
Understanding Data Skew: The Root Cause of Task Failures
What is Data Skew?
Data skew is a common challenge in distributed data processing platforms like Apache Spark and Databricks. It occurs when certain partitions of data hold significantly more records than others, creating an imbalanced workload distribution across your cluster.
Identifying Data Skew Symptoms
Before fixing skew, you need to know how to spot it. Fortunately, Spark and Databricks provide several ways to detect whether uneven data distribution is slowing down your jobs:
| Symptom | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Running Tasks | In a healthy Spark job, tasks within the same stage should finish in roughly the same amount of time. When you see a few tasks taking dramatically longer than the rest, that’s a classic sign of skew | Prolonged job execution |
| Memory Spill | Spill is what happens when Spark runs low on memory. It starts to move data from memory to disk, and this can be quite expensive | Performance degradation |
| Executor Failures | Databricks automatically retries failed tasks, often on the same executor with the same oversized partition. Tasks fail repeatedly until reaching the maximum retry threshold | Job failures |
| Uneven Resource Utilization | Some executors remain idle while others are overloaded | Wasted cluster resources |
Common Failure Patterns
Most Spark job failures fall into a surprisingly small set of patterns. Once you learn to recognize these patterns — shuffle explosion, memory errors, data skew, executor loss, and serialization issues — you can debug problems dramatically faster:
- Memory-related failures: ExecutorLostFailure (executor exited caused by one of the running tasks)
- Reason: Remote RPC client disassociated. Likely due to containers exceeding thresholds, or network issues
- Task retry cycles: Failed tasks continuously retry on the same problematic partition
- Resource exhaustion: For memory intensive workloads, configure fewer cores per Databricks executor. This allocates more memory per concurrent task
The Performance Impact of Data Distribution Problems
Quantifying the Cost
The performance impact of data skew can be dramatic. In one documented case, replacing coalesce(1) with repartition(1) reduced execution time from 4 hours and 30 minutes to just 18 minutes—a 93% improvement in performance.
Why Traditional Solutions Fall Short
Teams respond by increasing executor memory, which costs more but doesn’t solve the underlying distribution problem. You’re treating symptoms instead of causes. This approach leads to:
- Increased infrastructure costs without proportional performance gains
- Continued task failures despite additional resources
- Inefficient cluster utilization
- Longer development cycles due to debugging overhead
Comprehensive Repartitioning Strategies
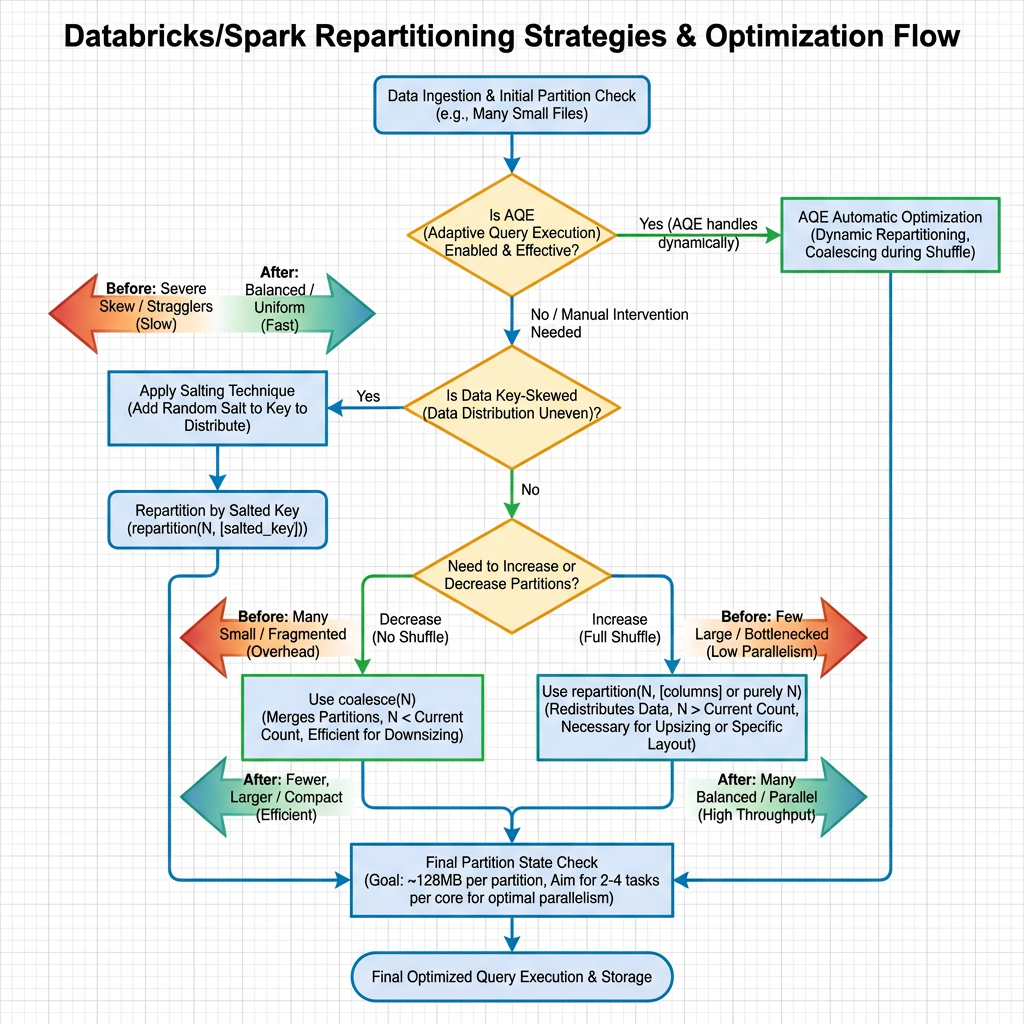
1. Repartition vs. Coalesce: Choosing the Right Approach
Understanding when to use
| Method | Use Case | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| repartition() | Balances the join by region, while coalesce() reduces partitions for a clean output | Full shuffle operation, better for balancing |
| coalesce() | Coalesce avoids a full shuffle | No shuffle, faster for reducing partitions |
Best Practice: Use 2–4 partitions per core, adjusted for data size
2. Advanced Techniques: Salting for Skewed Keys
Use salting for key-based operations: This is an easy, effective way to evenly distribute skewed keys across partitions. The salting technique involves:
- Adding a random salt value to skewed keys
- Distributing data more evenly across partitions
- Performing operations on the salted data
- Removing the salt in final results
3. Adaptive Query Execution (AQE): Automatic Optimization
Adaptive query execution (AQE) is query re-optimization that occurs during query execution. The motivation for runtime re-optimization is that Databricks has the most up-to-date accurate statistics at the end of a shuffle and broadcast exchange.
Key AQE Benefits:
- Databricks can opt for a better physical strategy, pick an optimal post-shuffle partition size and number, or do optimizations that used to require hints, for example, skew join handling
- 1Spark 3.0+ automatically handles many skew-related issues
- Runtime statistics enable better decision-making
4. Partition Size Optimization
Databricks recommends all partitions contain at least a gigabyte of data. Tables with fewer, larger partitions tend to outperform tables with more, smaller partitions.
Optimization Guidelines:
| Scenario | Recommended Strategy | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Large datasets | Use repartition() with optimal partition count | Ensures balanced distribution |
| Small datasets | Use coalesce() to reduce partitions | Avoids unnecessary shuffle overhead |
| Join operations | Apply repartitioning before joins | Minimizes shuffle during join execution |
| Write operations | Optimize partition count for output format | Balances file size and parallelism |
MinervaDB’s Approach to Databricks Optimization
Expert Data Engineering Solutions
MinervaDB Engineering Services stands as a premier provider of comprehensive data engineering solutions, delivering expert consulting and end-to-end solutions from initial architecture design to ongoing optimization and support.
Specialized Databricks Services
Organizations looking to adopt dynamic assortment planning on Databricks can follow a phased approach, achieving 30% faster decision cycle for assortment reviews. MinervaDB’s approach includes:
- Performance Analysis: Identifying bottlenecks and skew patterns
- Architecture Optimization: Designing efficient data distribution strategies
- Monitoring Implementation: Setting up comprehensive observability
- Cost Optimization: Transforming database operations into strategic assets for measurable ROI and efficiency gains
Comprehensive Database Expertise
MinervaDB’s Remote DBA Subscription Plan delivers expert support across a comprehensive range of open-source database technologies, including specialized expertise in performance optimization and scalability engineering.
Implementation Best Practices
1. Monitoring and Detection
Implement comprehensive monitoring to detect skew early:
- Task Duration Analysis: Monitor task execution times within stages
- Memory Usage Tracking: Watch for spill indicators
- Partition Size Monitoring: Ensure balanced data distribution
- Resource Utilization: Track executor efficiency
2. Proactive Optimization Strategies
| Strategy | Implementation | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-processing | Apply repartitioning before expensive operations | Reduced shuffle overhead |
| Key Distribution Analysis | Identify and salt highly skewed keys | Balanced partition sizes |
| Adaptive Configuration | Enable AQE for automatic optimization | Runtime performance improvements |
| Resource Tuning | Configure fewer cores per Databricks executor for memory-intensive workloads | Better memory allocation per task |
3. Code Implementation Examples
Detecting Skew:
# Monitor partition sizes df.rdd.mapPartitions(lambda x: [sum(1 for _ in x)]).collect()
Applying Repartitioning:
# For balanced distribution df_balanced = df.repartition(num_partitions, "key_column") # For reducing partitions without shuffle df_coalesced = df.coalesce(target_partitions)
Implementing Salting:
from pyspark.sql.functions import rand, concat, lit
# Add salt to skewed keys
df_salted = df.withColumn("salted_key",
concat(col("skewed_key"),
lit("_"),
(rand() * 10).cast("int")))
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Memory Management
The Databricks driver node coordinates your entire Spark application. It maintains the SparkContext, schedules jobs, coordinates tasks across executors, manages application metadata, collects results. Common memory issues include:
- Driver Memory: Avoid collecting large datasets to driver
- Executor Memory: Balance memory allocation with core counts
- Broadcast Variables: Monitor size of broadcast operations
Performance Tuning
Whether you’re optimizing a nightly ETL job or troubleshooting a stubborn DataFrame, understanding how to use repartitioning wisely is crucial:
- Profile Before Optimizing: Use Spark UI to identify bottlenecks
- Test Different Strategies: Compare repartition vs. coalesce performance
- Monitor Resource Usage: Track CPU, memory, and I/O utilization
- Validate Results: Ensure data integrity after optimization
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
Performance Metrics
| Metric | Target | Monitoring Method |
|---|---|---|
| Task Duration Variance | < 20% difference between fastest and slowest tasks | Spark UI Stages tab |
| Memory Spill | Zero or minimal spill to disk | Stage details in Spark UI |
| Executor Utilization | > 80% average utilization across cluster | Cluster metrics dashboard |
| Job Completion Time | Baseline improvement of 30-50% | Historical job performance data |
Cost Optimization Results
Effective repartitioning strategies typically deliver:
- 30-70% reduction in job execution time
- 20-40% decrease in cluster resource requirements
- Significant cost savings through improved efficiency
- Enhanced reliability with fewer task failures
Conclusion: Building Resilient Data Pipelines
High task failures and data skew in Databricks environments are solvable challenges when approached with the right strategies and expertise. Start by identifying skew using Spark UI or custom logic to identify which keys or partitions are causing the issue, then leverage Adaptive Query Execution as Spark 3.0+ automatically handles many skew-related issues.
The key to success lies in:
- Early Detection: Implementing comprehensive monitoring to identify skew patterns
- Strategic Repartitioning: Choosing the right technique for your specific use case
- Continuous Optimization: Regularly reviewing and tuning your data distribution strategies
- Expert Guidance: Partnering with specialists like MinervaDB for complex optimization challenges
By implementing these strategies and maintaining a proactive approach to data distribution optimization, organizations can build resilient, high-performance data pipelines that scale efficiently and deliver consistent results.
Ready to optimize your Databricks performance? Consider partnering with MinervaDB’s expert data engineering team to implement these strategies and achieve measurable performance improvements in your data infrastructure.


