MySQL “Got an Error Reading Communication Packet”: Complete Troubleshooting Guide – MySQL Error Reading Communication Packet
The “Got an error reading communication packet” error, also known as MySQL Error Reading Communication Packet, is one of the most frustrating issues MySQL administrators encounter. This error typically appears in MySQL error logs and can cause application timeouts, connection drops, and database instability. Understanding its root causes and implementing the right solutions is crucial for maintaining a robust MySQL environment.
What Is the “Got an Error Reading Communication Packet” Error?
This error occurs when MySQL cannot properly read data packets sent between the client and server. The communication packet represents data transmitted during database operations, including SQL queries, result sets, and binary log events in replication scenarios.
The MySQL Error Reading Communication Packet issue can lead to various operational challenges, and recognizing its signs early can save time and resources.
When MySQL encounters this error, it often closes the connection immediately, leading to the dreaded “Lost connection to MySQL server during query” error that applications experience.
Primary Causes of Communication Packet Errors
1. max_allowed_packet Configuration Issues
The most common cause is an inadequate max_allowed_packet setting. This MySQL variable determines the maximum size of packets that can be transmitted between client and server.
When this occurs:
- Large queries or result sets exceed the packet size limit
- BLOB or TEXT data insertions fail
- Import operations with large datasets terminate unexpectedly
2. Network Connectivity Problems
Network instability frequently triggers communication packet errors. Common network-related causes include:
- Intermittent connection drops
- High network latency
- Firewall interference
- Router or switch configuration issues
3. Server Resource Constraints
Insufficient server resources can cause MySQL to terminate connections:
- Low available RAM
- Inadequate swap space
- High CPU utilization
- Operating system process limits
4. Large Query Operations
Complex queries processing large datasets may exceed timeout limits or packet size restrictions, particularly when:
- Performing bulk data imports
- Executing queries with large result sets
- Working with substantial BLOB data
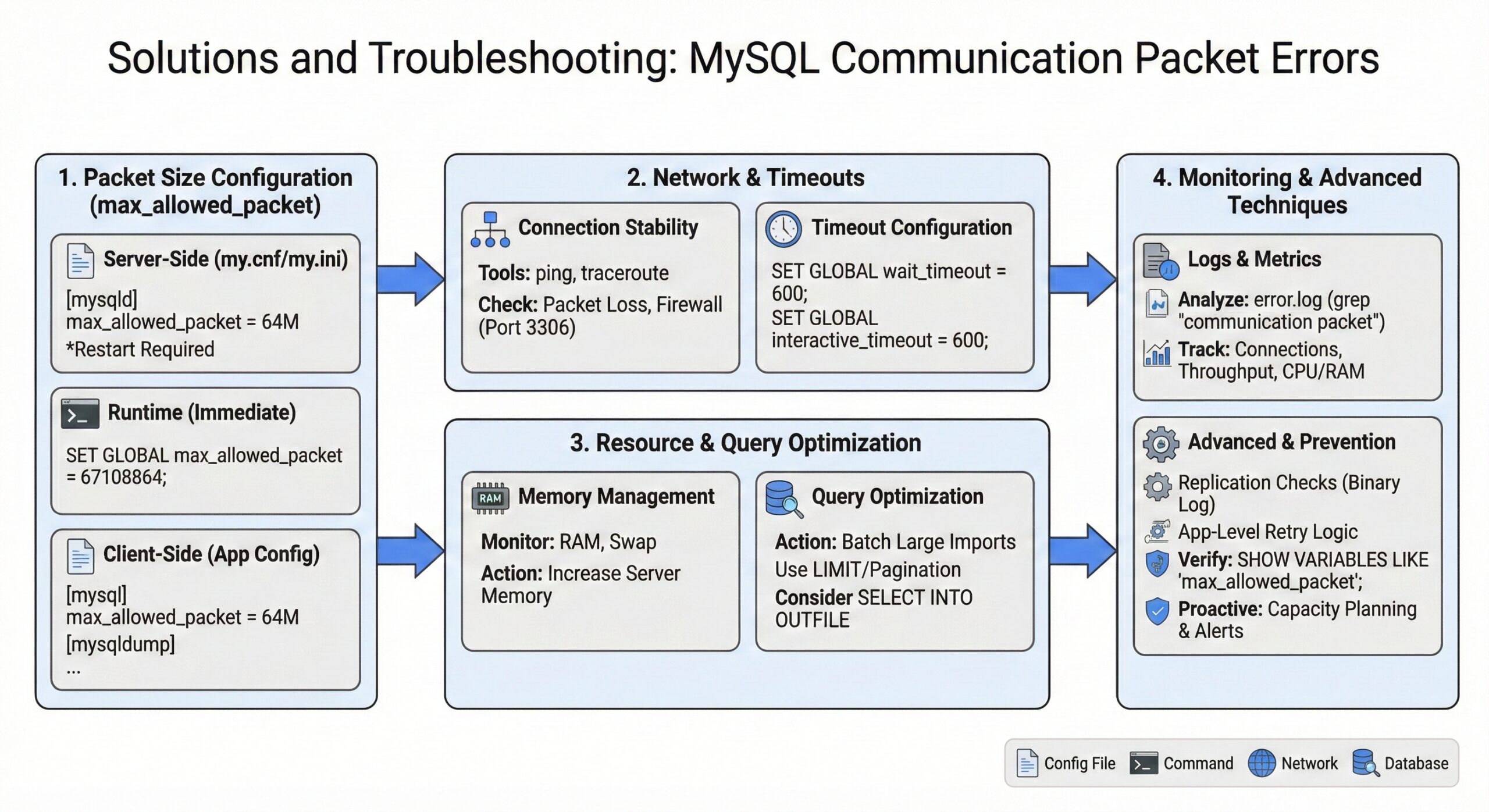
Solutions and Troubleshooting Steps
Adjusting max_allowed_packet Settings
Server-Side Configuration
Modify the MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini):
[mysqld] max_allowed_packet = 64M
Important considerations:
- The [mysqld] section is required for MySQL 5.5+
- Restart MySQL service after configuration changes
- Maximum theoretical limit is 1GB
Runtime Configuration
Set the variable dynamically for immediate effect:
SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet = 67108864; -- 64MB in bytes
Client-Side Configuration
Configure client applications to handle large packets:
[mysql] max_allowed_packet = 64M [mysqldump] max_allowed_packet = 64M
Network Troubleshooting
Connection Stability Testing
Monitor network connectivity between client and server:
- Use ping and traceroute for basic connectivity testing
- Check for packet loss during peak usage periods
- Verify firewall rules allow MySQL traffic (default port 3306)
Timeout Configuration
Adjust MySQL timeout settings to accommodate network latency:
SET GLOBAL wait_timeout = 600; SET GLOBAL interactive_timeout = 600;
Resource Optimization
Memory Management
Ensure adequate system resources:
- Monitor available RAM and swap space
- Check for memory-intensive processes competing with MySQL
- Consider increasing server memory for high-traffic environments
Query Optimization
Optimize large data operations:
- Break large imports into smaller batches
- Use LIMIT clauses for large result sets
- Implement pagination for web applications
- Consider using SELECT INTO OUTFILE for large exports
Monitoring and Prevention
Error Log Analysis
Regularly review MySQL error logs for patterns:
tail -f /var/log/mysql/error.log | grep "communication packet"
Performance Monitoring
Track key metrics:
- Connection counts and duration
- Query execution times
- Network throughput
- Server resource utilization
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Replication-Specific Issues
For MySQL replication environments, communication packet errors may indicate:
- Binary log events exceeding packet limits
- Network issues between master and slave servers
- Slave server resource constraints
Application-Level Solutions
Implement robust error handling in applications:
- Connection retry logic with exponential backoff
- Query timeout configuration
- Connection pooling optimization
- Graceful degradation for temporary connectivity issues
Configuration Verification
Verify current settings to ensure changes take effect:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'max_allowed_packet'; SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Aborted_connects';
Best Practices for Prevention
Proactive Configuration
- Set appropriate max_allowed_packet values based on your data requirements
- Configure both server and client settings consistently
- Test configuration changes in development environments first
Regular Maintenance
- Monitor error logs for early warning signs
- Update network infrastructure to ensure reliability
- Perform regular database maintenance to optimize performance
Capacity Planning
- Assess data growth patterns to anticipate packet size requirements
- Plan for peak usage scenarios with adequate resource allocation
- Implement monitoring alerts for connection and packet-related errors
Conclusion
The “Got an error reading communication packet” error in MySQL typically stems from max_allowed_packet configuration issues, network problems, or resource constraints. By systematically addressing each potential cause—adjusting packet size limits, ensuring network stability, and optimizing server resources—you can resolve these errors and maintain a stable MySQL environment.
Regular monitoring and proactive configuration management are essential for preventing these issues from impacting your applications. Remember that the specific solution may vary based on your environment, so thorough testing and gradual implementation of changes will ensure optimal results.
Further Reading
- Understanding Cloud-Native Databases: A Complete Guide for Modern Applications
- PostgreSQL VACUUM Guide: Complete Best Practices for Database Maintenance
- 25 Advanced MySQL DBA Questions and Answers: Master Database Administration
- Generating Numeric Sequences in MySQL: A Comprehensive Guide
- Best Practices for Managing MongoDB Log Files and System Resources
- MySQL Communication Errors