Vertica Index Usage and Troubleshooting Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide
Vertica’s approach to indexing differs significantly from traditional relational databases, making it essential for database administrators and developers to understand its unique architecture and optimization strategies. This comprehensive guide explores Vertica’s indexing mechanisms, best practices for usage, and effective troubleshooting techniques to ensure optimal database performance.
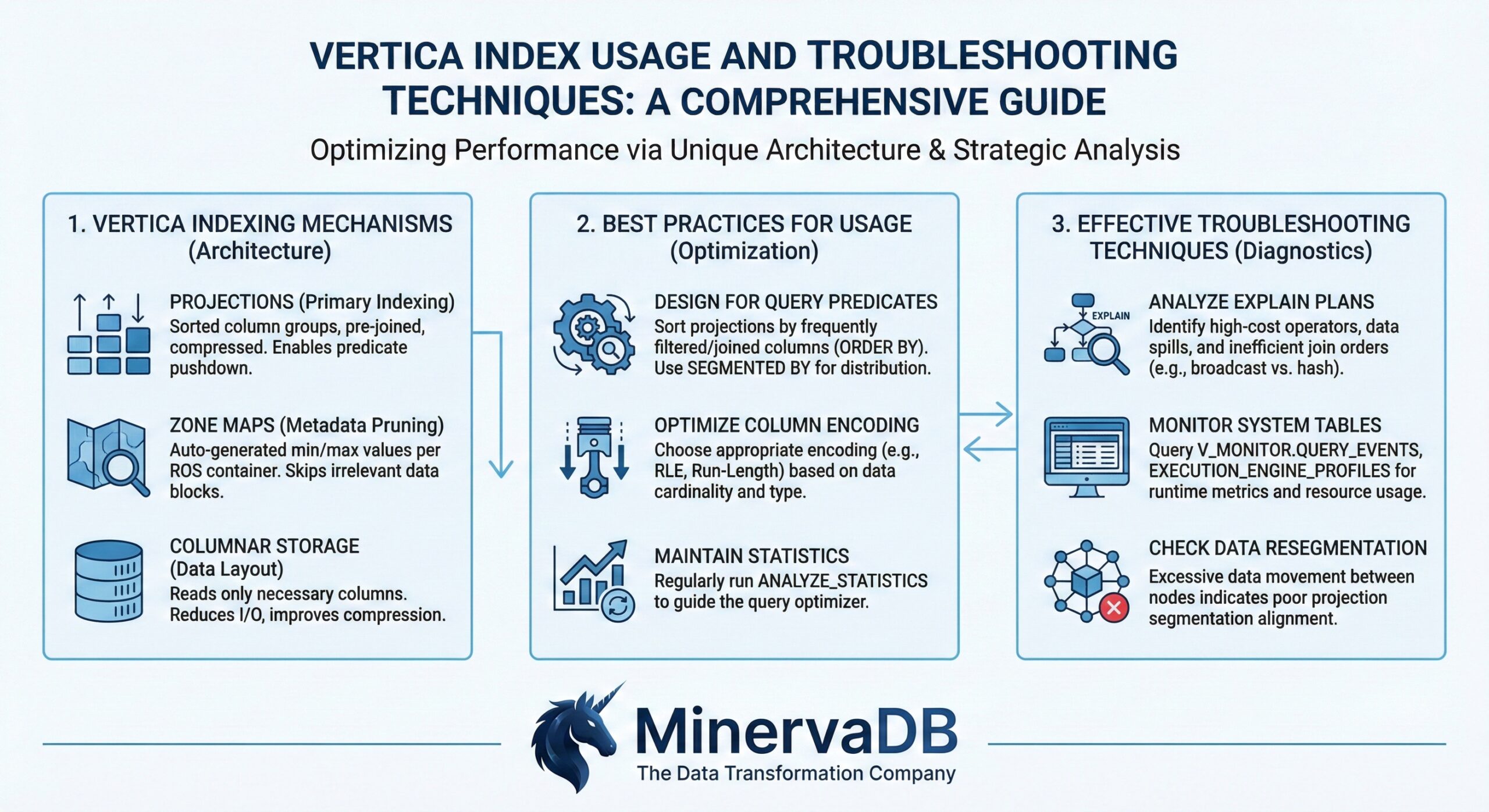
Understanding Vertica’s Indexing Architecture
Unlike traditional databases that rely on separate index structures, Vertica uses projections as its primary indexing mechanism. Projections are physical storage structures that contain sorted, compressed copies of table data, effectively serving as both storage and indexing layers. This columnar approach allows Vertica to achieve exceptional query performance through intelligent data organization and compression.
Core Indexing Components
Projections as Primary Indexes Projections in Vertica function as clustered indexes, where data is physically sorted and stored according to specified sort orders. The sort order of a projection determines how efficiently queries can access data, making it crucial for performance optimization.
Secondary Index Types While projections handle most indexing needs, Vertica also supports specialized indexes:
- Text Indexes: Created using CREATE TEXT INDEX for full-text search capabilities
- Spatial Indexes: Generated with STV_Create_Index for geospatial operations
Best Practices for Index Usage
Optimal Sort Order Design
The foundation of effective Vertica indexing lies in choosing appropriate sort orders for projections. Consider these best practices:
Prioritize High-Selectivity Columns Place columns with high selectivity (many distinct values) early in the sort order to maximize query performance. This allows Vertica to quickly eliminate irrelevant data during query execution.
Leverage Low-Cardinality Columns for Compression Position low-cardinality columns strategically in the sort order to maximize Run-Length Encoding (RLE) compression benefits. This approach minimizes storage requirements while maintaining query performance.
Align Sort Order with Query Patterns Design projection sort orders to match your most frequent query patterns, particularly those involving WHERE clauses, JOIN conditions, and GROUP BY operations.
Database Designer Optimization
Vertica’s Database Designer is an essential tool for index optimization. It analyzes query workloads and recommends optimal projection designs, including:
- Sort order recommendations based on query patterns
- Compression encoding suggestions
- Segmentation strategies for distributed environments
- Projection consolidation opportunities
Comprehensive Design Process Use Database Designer’s comprehensive setting to globally optimize your database. This process analyzes all tables and creates projections optimized for both query performance and data compression.
Incremental Design Updates For evolving workloads, run Database Designer incrementally to create additional projections for new query patterns without disrupting existing optimizations.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Query Plan Analysis
Understanding query execution plans is fundamental to index troubleshooting. Use the EXPLAIN statement to analyze how Vertica processes queries and identify indexing issues.
Basic Query Plan Analysis
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column_name = 'value';
This command reveals which projections Vertica uses and whether optimal indexes are being leveraged.
Annotated Query Plans Use EXPLAIN ANNOTATED to generate optimizer hints that encapsulate the query plan, providing deeper insights into index usage patterns.
System Table Monitoring
Vertica provides comprehensive system tables for monitoring index performance and identifying issues.
Projection Storage Monitoring The PROJECTION_STORAGE system table monitors disk storage usage by each projection on each node:
SELECT projection_name, node_name, used_bytes, ros_count FROM projection_storage WHERE projection_name LIKE '%your_table%' ORDER BY used_bytes DESC;
Query Performance Analysis Monitor query execution patterns using system tables to identify projections that may need optimization.
Performance Monitoring Strategies
Real-Time Profiling Implement real-time profiling to monitor long-running queries and identify index-related bottlenecks. Use system tables to observe executing operators within query plans across cluster nodes.
Workload Analysis Regularly analyze workload patterns to ensure projections remain optimized for current query demands. This proactive approach helps identify when projection redesign may be necessary.
Common Issues and Solutions
Suboptimal Projection Usage
Problem: Queries not using the most efficient projections Solution: Analyze query plans using EXPLAIN and redesign projections with appropriate sort orders
Problem: High storage usage with poor compression Solution: Optimize sort orders to leverage RLE encoding for low-cardinality columns
Index Maintenance Issues
Problem: Outdated statistics affecting query optimization Solution: Regularly update statistics using Database Designer’s “Update Statistics” option
Problem: Projection fragmentation impacting performance Solution: Monitor ROS (Read Optimized Store) counts in PROJECTION_STORAGE and consider mergeout operations
Advanced Troubleshooting Commands
Projection Analysis Commands
Check Projection Sort Order
SELECT GET_PROJECTION_SORT_ORDER('projection_name');
This function returns the order of columns in a projection’s ORDER BY clause.
Monitor Projection Health
SELECT * FROM projections WHERE projection_name LIKE '%table_name%' AND is_up_to_date = false;
Analyze Column Storage Use system tables to monitor column-level storage usage and identify compression opportunities.
Performance Optimization Workflow
- Baseline Analysis: Use EXPLAIN to understand current query execution patterns
- Workload Profiling: Analyze query patterns using system tables
- Design Optimization: Run Database Designer to generate recommendations
- Implementation: Deploy optimized projections based on recommendations
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor performance using system tables
- Iteration: Regularly reassess and optimize based on changing workload patterns
Monitoring and Maintenance Best Practices
Proactive Monitoring
Establish regular monitoring routines using Vertica’s system tables to identify potential issues before they impact performance. Focus on:
- Projection storage utilization trends
- Query execution patterns and performance metrics
- Index usage statistics and efficiency measures
Maintenance Scheduling
Implement regular maintenance schedules that include:
- Statistics updates through Database Designer
- Projection health assessments
- Storage optimization reviews
- Query pattern analysis
Conclusion
Effective Vertica index usage and troubleshooting requires understanding the unique projection-based architecture and leveraging appropriate tools and techniques. By following the best practices outlined in this guide—from optimal sort order design to comprehensive monitoring strategies—database administrators can ensure optimal performance and quickly resolve indexing issues.
The key to success lies in proactive monitoring, regular optimization through Database Designer, and thorough understanding of query execution patterns. With these techniques, organizations can maximize the performance benefits of Vertica’s innovative indexing approach while maintaining system reliability and efficiency.
Remember that Vertica’s indexing strategy is fundamentally different from traditional databases, and success requires embracing this columnar, projection-based approach rather than attempting to apply conventional indexing concepts. Regular analysis, optimization, and monitoring form the foundation of effective Vertica index management.


