PostgreSQL 16 for DBAs: Essential Features and Practical Implementation Guide – Exploring PostgreSQL 16 New Features
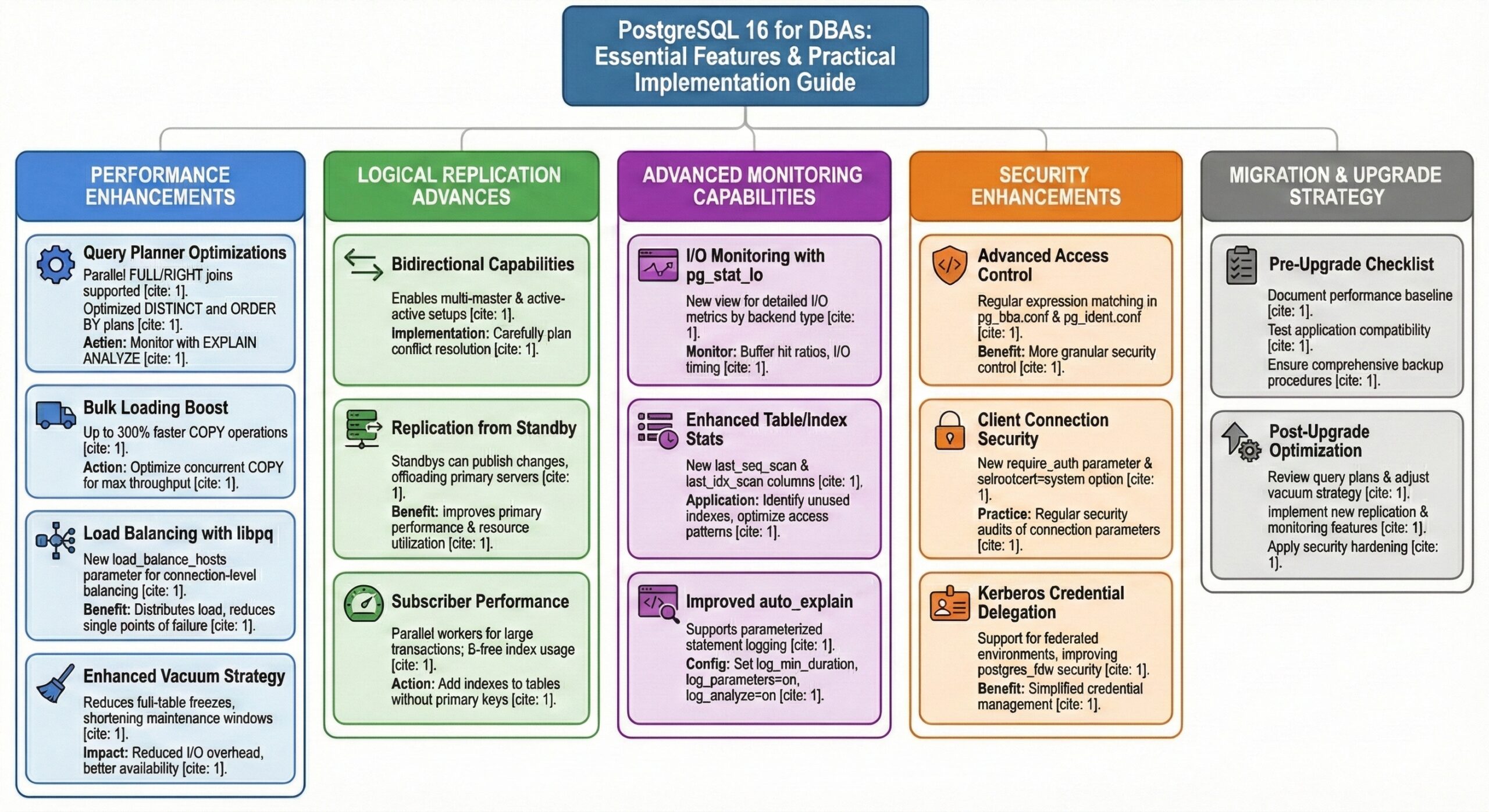
PostgreSQL 16 represents a significant leap forward for database administrators, delivering performance enhancements, advanced replication capabilities, and robust monitoring tools that directly impact daily operations. This comprehensive guide explores the key features every PostgreSQL DBA should understand and implement.
This guide highlights the PostgreSQL 16 New Features that enhance functionality and efficiency, making them vital for every DBA to explore.
Performance Enhancements That Matter for DBAs: Key Insights on PostgreSQL 16 New Features for DBAs
Query Planner Optimizations
PostgreSQL 16 introduces substantial improvements to the query planner that can dramatically reduce query execution times. The planner now supports parallelization of FULL and RIGHT joins, which is particularly beneficial for data warehousing and analytical workloads.
Practical Implementation:
- Monitor query performance using EXPLAIN ANALYZE to identify queries that benefit from parallel joins
- Review existing queries with DISTINCT and ORDER BY clauses, as these now generate more optimized execution plans
- Test window function performance in your environment, as optimizations can significantly improve reporting queries
Bulk Loading Performance Boost
The 300% performance improvement in bulk loading operations using the COPY command is a game-changer for DBAs managing large data imports and ETL processes.
Implementation Strategy:
- Benchmark your current COPY operations before upgrading
- Optimize concurrent COPY operations for maximum throughput
- Consider restructuring batch processing jobs to leverage improved bulk loading capabilities
- Test both single and concurrent COPY scenarios in your environment
Load Balancing with libpq
The new load_balance_hosts parameter enables connection-level load balancing, essential for high-availability setups.
Configuration Example:
-- Connection string with load balancing psql "host=server1,server2,server3 port=5432 dbname=mydb user=myuser load_balance_hosts=random"
DBA Benefits:
- Distribute connection load across multiple servers
- Improve application resilience
- Reduce single points of failure in connection management
Enhanced Vacuum Strategy
PostgreSQL 16 reduces the need for full-table freezes, minimizing maintenance windows and improving system availability.
Operational Impact:
- Shorter maintenance windows
- Reduced I/O overhead during vacuum operations
- Better performance for high-transaction databases
- More predictable vacuum scheduling
Logical Replication Advances for Modern Architectures
Bidirectional Replication Capabilities
Bidirectional logical replication opens new possibilities for multi-master configurations and disaster recovery scenarios.
Use Cases for DBAs:
- Active-active database configurations
- Geographic data distribution
- Enhanced disaster recovery strategies
- Collaborative data environments
Implementation Considerations:
- Carefully plan conflict resolution strategies
- Monitor replication lag closely
- Test failover scenarios thoroughly
- Implement proper monitoring for bidirectional flows
Logical Replication from Standby
This feature allows standby servers to publish logical changes, reducing load on primary servers and improving resource utilization.
Practical Benefits:
- Offload replication overhead from primary servers
- Improve primary server performance
- Create more flexible replication topologies
- Better resource distribution in complex environments
Performance Enhancements for Subscribers
Parallel workers for large transactions and B-tree index usage instead of sequential scans significantly improve subscriber performance.
DBA Action Items:
- Review tables without primary keys and consider adding appropriate indexes
- Monitor subscriber performance metrics
- Optimize worker configurations for parallel processing
- Test large transaction handling in development environments
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
I/O Monitoring with pg_stat_io
The new pg_stat_io view provides detailed I/O metrics crucial for performance tuning.
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- I/O access patterns by backend type
- Buffer hit ratios across different contexts
- I/O timing statistics
- Storage subsystem performance insights
Implementation:
-- Monitor I/O patterns SELECT backend_type, object, context, reads, writes, extends FROM pg_stat_io WHERE backend_type = 'client backend';
Enhanced Table and Index Statistics
New timestamp columns last_seq_scan and last_idx_scan provide better insights into access patterns.
Practical Applications:
- Identify unused indexes for removal
- Optimize table access patterns
- Plan maintenance windows based on usage patterns
- Monitor query performance trends
Improved auto_explain Functionality
Enhanced auto_explain with parameterized statement logging improves troubleshooting capabilities.
Configuration for DBAs:
-- Enable auto_explain with parameters LOAD 'auto_explain'; SET auto_explain.log_min_duration = 1000; SET auto_explain.log_parameters = on; SET auto_explain.log_analyze = on;
Security Enhancements for Enterprise Environments
Advanced Access Control
Regular expression matching in pg_hba.conf and pg_ident.conf provides more granular security control.
Implementation Examples:
# Regular expression matching for user groups host all /^app_user_.*$ 192.168.1.0/24 md5 host analytics /^analyst_.*$ 10.0.0.0/8 scram-sha-256
Client Connection Security
The require_auth parameter and sslrootcert=system option enhance connection security.
Security Best Practices:
- Implement require_auth for critical applications
- Use system certificate stores for SSL validation
- Regular security audits of connection parameters
- Monitor authentication failures and patterns
Kerberos Credential Delegation
Support for Kerberos credential delegation improves security for federated database environments.
Enterprise Benefits:
- Seamless integration with existing Kerberos infrastructure
- Enhanced security for postgres_fdw connections
- Simplified credential management
- Better compliance with enterprise security policies
Migration and Upgrade Strategy
Pre-Upgrade Checklist
- Performance Baseline: Document current performance metrics
- Compatibility Testing: Test applications with PostgreSQL 16
- Backup Strategy: Ensure comprehensive backup procedures
- Monitoring Setup: Prepare monitoring for new features
- Security Review: Update security configurations
Post-Upgrade Optimization
- Query Plan Analysis: Review and optimize query plans
- Vacuum Strategy: Adjust vacuum parameters for new improvements
- Replication Configuration: Implement new replication features
- Monitoring Integration: Utilize new monitoring capabilities
- Security Hardening: Apply enhanced security features
Conclusion
PostgreSQL 16 delivers significant value for database administrators through performance improvements, advanced replication capabilities, enhanced monitoring, and robust security features. The combination of query planner optimizations, improved bulk loading, and sophisticated monitoring tools provides DBAs with powerful capabilities to manage modern database environments effectively.
The upgrade to PostgreSQL 16 represents not just a version update, but a strategic enhancement to your database infrastructure. By implementing these features systematically and monitoring their impact, DBAs can achieve substantial improvements in performance, reliability, and security.
Start planning your PostgreSQL 16 migration today to leverage these powerful enhancements and stay ahead in database management excellence.
Further Reading
- PostgreSQL DELETE vs TRUNCATE: A Complete Guide to Data Removal Commands
- Mastering Google Cloud Dataflow and Apache Airflow Integration: A Comprehensive Guide for Data Engineers
- Mastering PostgreSQL Replication: A Complete Guide for Database Professionals
- Comprehensive Guide to MySQL to Amazon Redshift Data Replication Using Tungsten Replicator
- Useful CQLSH Commands for Everyday Use
- ClickHouse ReplacingMergeTree Explained