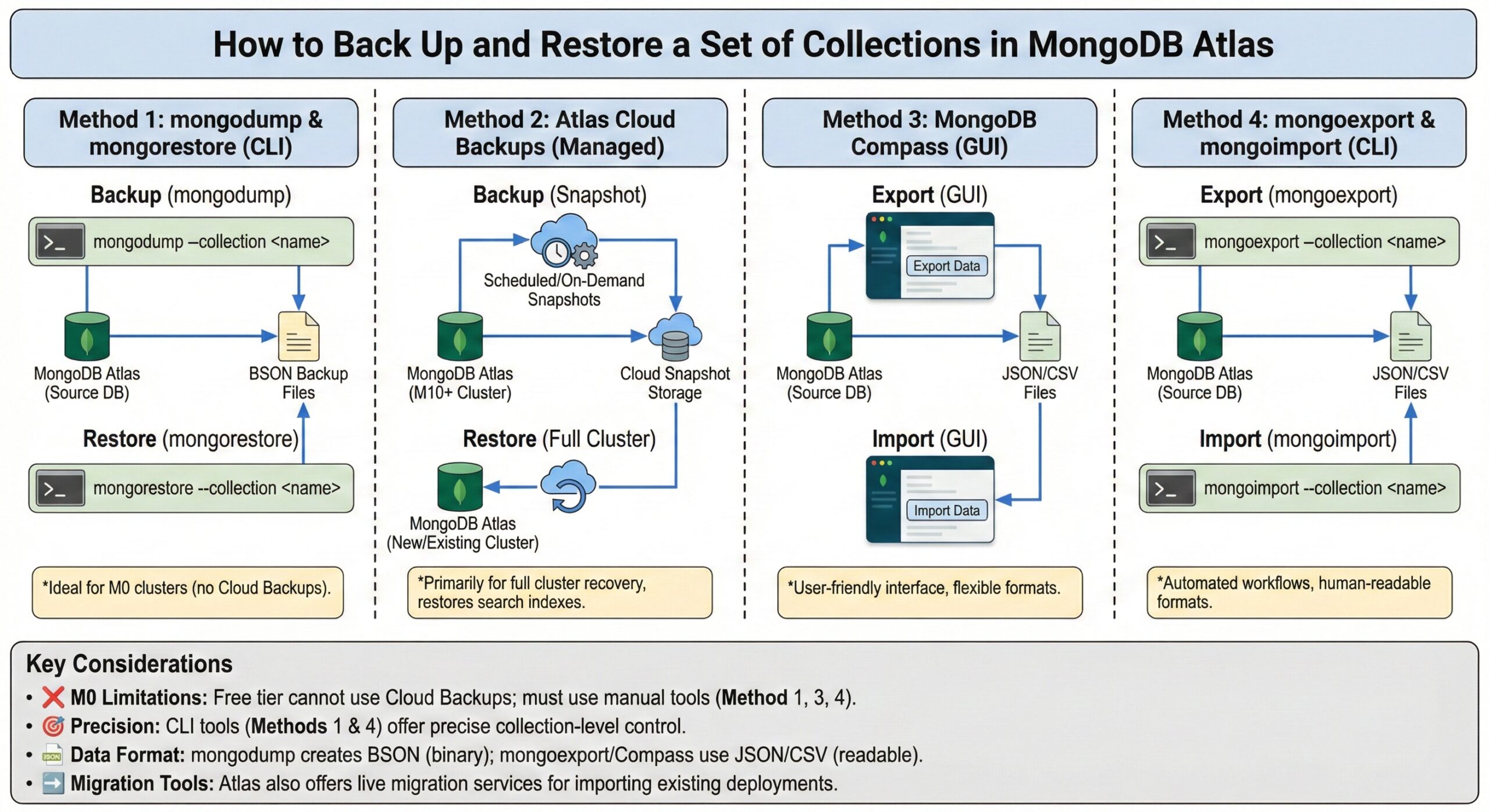
How to Back Up and Restore a Set of Collections in MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas offers several methods for backing up and restoring collections, depending on your cluster tier and specific requirements. Here are the main approaches:
Method 1: Using mongodump and mongorestore (Command Line Tools)
For Backup:
- Use mongodump with the –collection option to specify individual collections
- Include the –db parameter to specify the database
- Example: mongodump –host <connection-string> –db <database-name> –collection <collection-name>
For Restore:
- Use mongorestore with the –collection option to restore specific collections from backup files
- Example: mongorestore –host <connection-string> –db <database-name> –collection <collection-name> <backup-file-path>
This method is particularly useful for M0 clusters where Cloud Backups are not available.
Method 2: MongoDB Atlas Cloud Backups
Atlas provides fully managed and customizable backups using native snapshot capabilities of your cloud provider. These create full-copy snapshots with localized snapshot storage.
Key Features:
- Available for M10+ dedicated clusters
- Restores Atlas Search index definitions from Cloud Backup snapshots
- Supports both scheduled and on-demand snapshots
Note: Cloud Backups are primarily designed for full cluster recovery rather than individual collection restoration.
Method 3: MongoDB Compass (GUI Tool)
For Export:
- Use MongoDB Compass to export data from specific collections into JSON or CSV files
- Supports both JSON and CSV formats for flexible data handling
For Import:
- Import data from JSON or CSV files into existing or new collections
- Provides a user-friendly interface for collection-level operations
Method 4: mongoexport and mongoimport
For Export:
- mongoexport produces JSON or CSV exports of data from specific collections
- Run from the system command line for automated workflows
For Import:
- Use mongoimport to restore the exported data into MongoDB collections
- Supports the same JSON and CSV formats as mongoexport
Key Considerations
- M0 Cluster Limitations: Free tier clusters cannot use Cloud Backups and must rely on manual backup tools like mongodump and mongorestore
- Collection-Specific Control: Command-line tools (mongodump/mongorestore or mongoexport/mongoimport) provide more precise control for individual collection operations
- Data Format Differences: mongodump creates BSON files (binary format), while mongoexport and Compass work with human-readable JSON or CSV formats
- Atlas Migration Tools: Atlas also provides import capabilities for existing MongoDB deployments, JSON, or CSV files using live migration or self-guided tools
Choose the method that best fits your cluster tier, technical requirements, and whether you need full cluster or collection-specific backup and restore capabilities.
Further Reading
- Indexing Materialized Views in PostgreSQL
- Extracting and Substituting Text with Regular Expressions in PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL 18: Accelerating Disk Reads with Asynchronous I/O
- Strategic Shift from Oracle to PostgreSQL
- Cassandra Consistency Level Guide: Mastering Data Consistency in Distributed Systems