Extracting and Substituting Text with PostgreSQL Regular Expressions
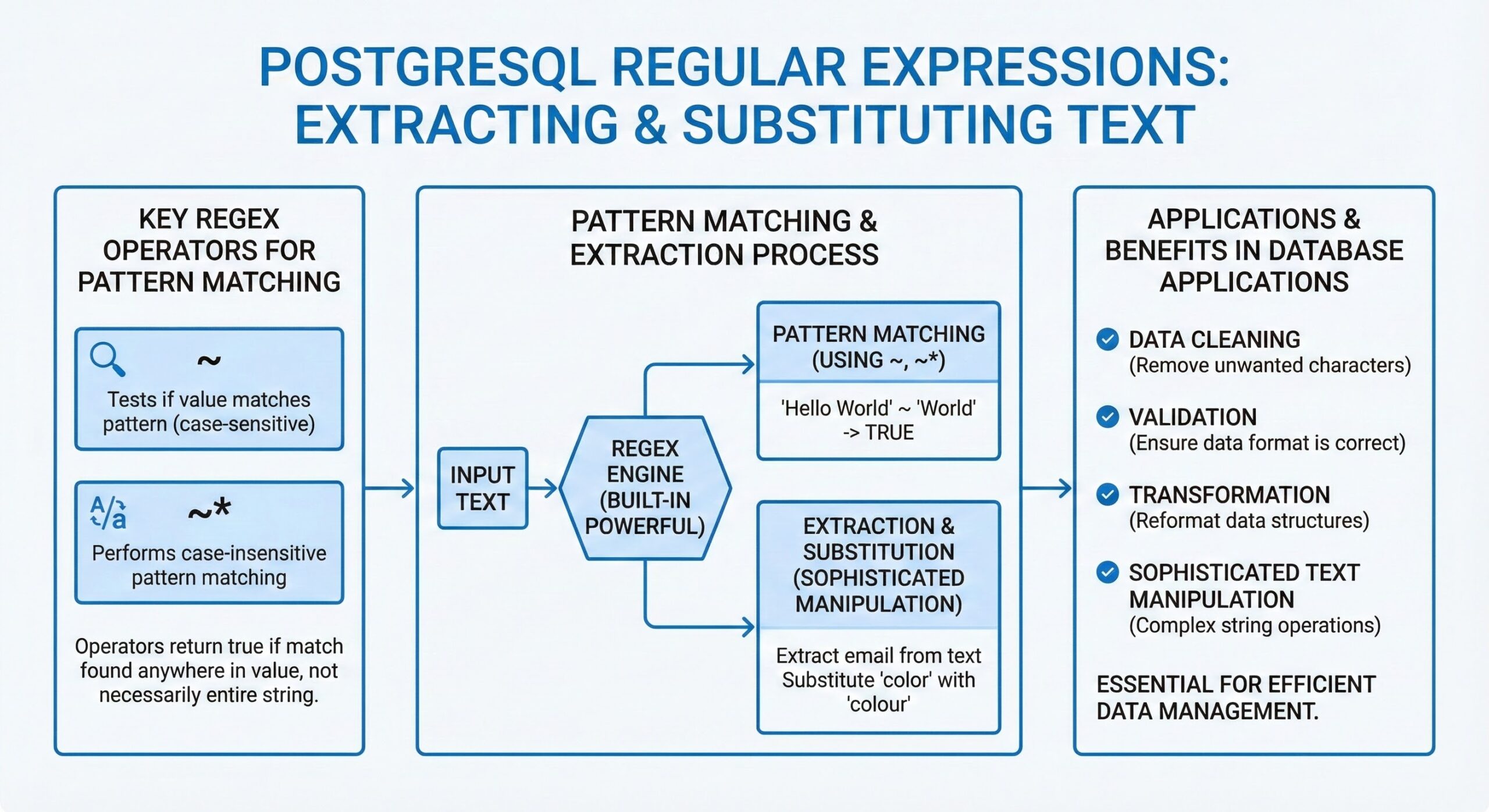
PostgreSQL provides a powerful built-in regex engine that enables sophisticated text manipulation through pattern matching, extraction, and substitution operations. Regular expressions are essential for data cleaning, validation, and transformation tasks in database applications. With native support for POSIX regular expressions, PostgreSQL offers a rich set of operators and functions that allow developers to perform complex string operations directly within SQL queries, reducing the need for external processing.
One of the core features is the ~ operator, which performs case-sensitive regular expression matching. For example, SELECT ‘abc123’ ~ ‘^abc’; returns true because the string starts with ‘abc’. Its counterpart !~ checks for non-matching patterns. Case-insensitive variants ~* and !~* are also available, enabling flexible text analysis without preprocessing. These operators integrate seamlessly into WHERE clauses, allowing pattern-based filtering of rows based on textual content.
PostgreSQL also supports the SIMILAR TO operator, which combines aspects of LIKE and full regular expressions. It allows the use of wildcards and character classes but with a more structured syntax. For instance, SELECT ‘abc’ SIMILAR TO ‘a%[c-z]’; evaluates to true, demonstrating its ability to blend simple patterns with regex-like constructs.
For extracting substrings that match a pattern, PostgreSQL provides regexp_match(), which returns an array of captured groups. For example, SELECT regexp_match(‘Email: <mailto:user@example.com>’, ‘([\w.-]+)@([\w.-]+)’); extracts the username and domain parts from an email address. When multiple matches exist, regexp_matches() with the ‘g’ flag can return all occurrences, making it useful for parsing logs or unstructured text.
The regexp_replace() function allows for advanced string substitution. It can replace parts of a string based on a regex pattern, with support for backreferences. For instance, SELECT regexp_replace(‘John Doe’, ‘(.*) (.*)’, ‘\\2, \\\1’); converts ‘John Doe’ into ‘Doe, John’. This is particularly useful for reformatting data during ETL processes.
Another valuable function is regexp_split_to_array(), which splits a string into an array using a regex as the delimiter. This is helpful when dealing with irregular delimiters in imported data. Similarly, regexp_split_to_table() returns each element of the split as a separate row, facilitating normalization of denormalized fields.
PostgreSQL’s regex engine supports a wide range of metacharacters, quantifiers, and character classes, including lookahead and lookbehind assertions in certain configurations. This depth of functionality makes it suitable for validating input formats (e.g., phone numbers, emails), sanitizing user-generated content, and transforming semi-structured data stored in text fields.
Overall, PostgreSQL’s regex capabilities empower database practitioners to handle real-world data challenges efficiently and declaratively within the database layer itself.
Key Regex Operators for Pattern Matching
PostgreSQL offers several operators for regex pattern matching:
- ~ operator: Tests if a value matches a regex pattern (case-sensitive)
- ~* operator: Performs case-insensitive pattern matching
These operators return true if the regex matches any part of the value, not necessarily the entire string.
Extracting Text with Regular Expressions
Using substring() Function
The substring(value from pattern) function extracts text based on a regex pattern. When the pattern includes capturing groups (), only the matched group content is returned.
-- Extract area code from phone number
SELECT substring('(416) 555-1212' from '\((\d{3})\)');
-- Returns: 416
Using regexp_match() Function
The regexp_match(value, pattern) function is more powerful for extracting multiple substrings simultaneously. It returns an array of captured groups, making it ideal for complex extractions.
-- Extract all parts of a phone number
SELECT regexp_match('(416) 555-1212', '^\D*(\d{3})\D*(\d{3})\D*(\d{4})\D*$');
-- Returns: {416,555,1212}
-- Access individual elements using array indexing
SELECT (regexp_match('(416) 555-1212', '^\D*(\d{3})\D*(\d{3})\D*(\d{4})\D*$'))[1] AS area_code;
-- Returns: 416
Substituting Text with Regular Expressions
Using regexp_replace() Function
The regexp_replace(value, regex, replacement, flags) function performs pattern-based text substitution. This function replaces occurrences of the regex pattern within the value with the specified replacement string.
-- Remove all non-digit characters from phone number
SELECT regexp_replace('(416) 555-1212', '\D', '', 'g');
-- Returns: 4165551212
Function Parameters
- value: The source text to process
- regex: The regular expression pattern to match
- replacement: The text to substitute for matched patterns
- flags: Optional modifiers that control matching behavior
Important Regex Flags
Understanding regex flags is crucial for effective text manipulation:
- “g” (Global): Replaces all matches, not just the first occurrence
- “i” (Case-insensitive): Ignores case when matching patterns
- “n” (Newline): Allows the . character to match newline characters
-- Without 'g' flag - replaces only first match
SELECT regexp_replace('hello world hello', 'hello', 'hi');
-- Returns: hi world hello
-- With 'g' flag - replaces all matches
SELECT regexp_replace('hello world hello', 'hello', 'hi', 'g');
-- Returns: hi world hi
Common Regex Patterns
Here are essential regex patterns for PostgreSQL text processing:
- .: Matches any single character
- \s: Matches whitespace characters, \S: matches non-whitespace
- \d: Matches digits, \D: matches non-digits
- \w: Matches word characters, \W: matches non-word characters
- ^: Matches start of string, $: matches end of string
- (): Creates capturing groups for extraction
- *: Matches 0 or more repetitions, +: matches 1 or more
- {N}: Matches exactly N repetitions
Practical Examples
-- Extract email domain
SELECT regexp_match('user@example.com', '@(.+)$');
-- Returns: {example.com}
-- Clean and format phone numbers
SELECT regexp_replace(
regexp_replace('1-416-555-1212', '\D', '', 'g'),
'(\d{1})(\d{3})(\d{3})(\d{4})',
'+\1 (\2) \3-\4'
);
-- Returns: +1 (416) 555-1212
-- Case-insensitive substitution
SELECT regexp_replace('Hello WORLD', 'hello', 'hi', 'gi');
-- Returns: hi WORLD
These regex functions provide PostgreSQL users with comprehensive text processing capabilities, enabling efficient data cleaning, validation, and transformation directly within the database layer.
Further Reading:
- PostgreSQL 18: Accelerating Disk Reads with Asynchronous I/O
- Strategic Shift from Oracle to PostgreSQL
- Cassandra Consistency Level Guide: Mastering Data Consistency in Distributed Systems
- Mastering MySQL EXPLAIN Format: Optimizing Query Performance in MySQL 8.0.32
- MySQL “Got an Error Reading Communication Packet”: Complete Troubleshooting Guide
- Regular Expression