Understanding Vector Indexes in MariaDB: HNSW, Distance Functions, and When to Use Them
MariaDB has emerged as a powerful platform for integrating vector search capabilities directly within a relational database environment, enabling efficient similarity searches for AI and machine learning applications. Central to this functionality are vector indexes, which differ fundamentally from traditional B-tree indexes by optimizing for approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) searches in high-dimensional spaces.
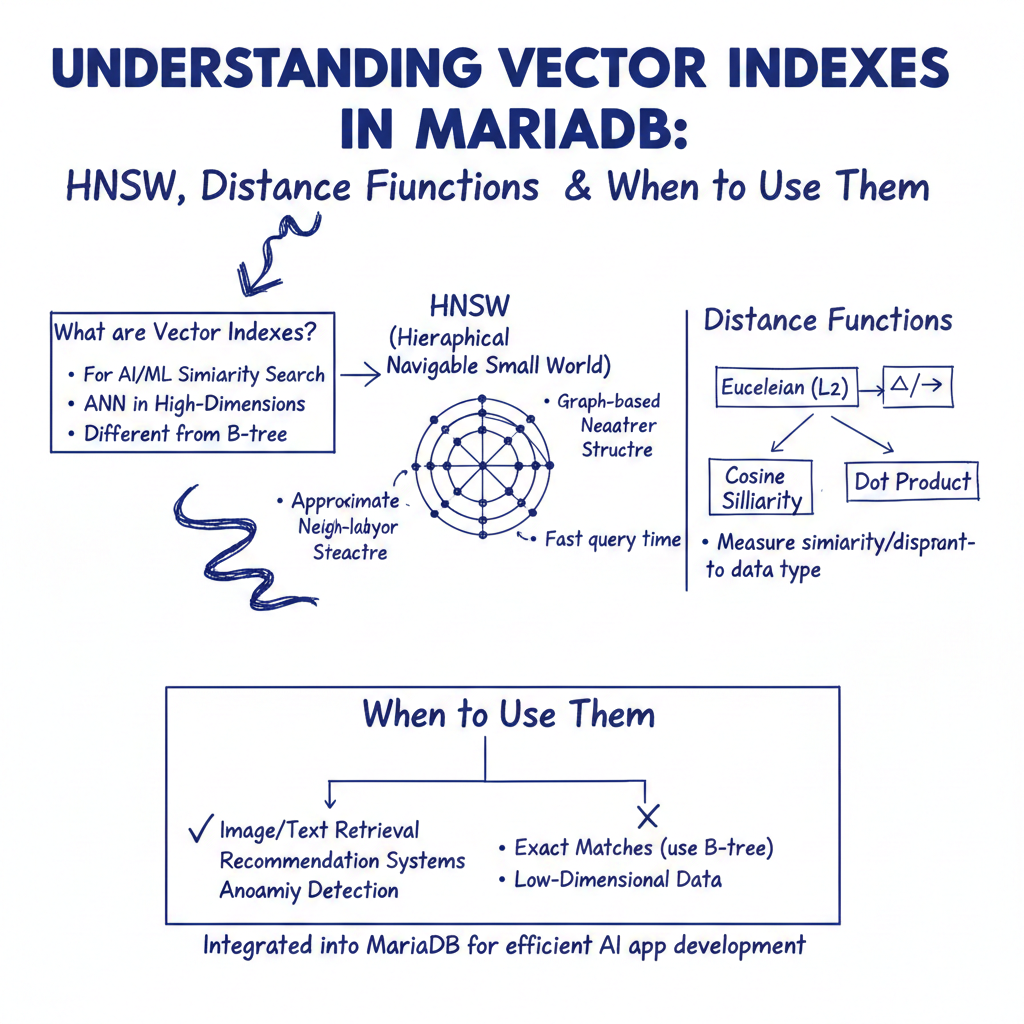
The HNSW Algorithm in MariaDB
MariaDB utilizes a variant of the Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds (HNSW) algorithm, specifically MHNSW, to power its vector indexing. This graph-based structure enables fast and scalable ANN searches by organizing vectors into hierarchical layers, allowing the search process to quickly navigate toward the most relevant results.
Unlike exact match indexes, HNSW returns approximate results, trading a small amount of accuracy for significant gains in speed and scalability. The performance and memory footprint of the index can be tuned using parameters such as M, which controls the number of connections per node in the graph, influencing the balance between search speed and index size.
Supported Distance Functions
MariaDB supports two primary distance functions for vector similarity:
- Euclidean Distance: Measures the straight-line distance between two points in vector space. It is sensitive to vector magnitude and is often suitable for numerical data where absolute differences matter.
- Cosine Distance: Measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors, focusing on orientation rather than magnitude. This makes it ideal for text embeddings and semantic search, where the relative direction of vectors captures meaning more effectively than their length.
The default distance function is Euclidean, but cosine can be explicitly specified during index creation.
When to Use Vector Indexes
Vector indexes in MariaDB are best suited for:
- Semantic Search: Finding documents or content based on meaning rather than keyword matching.
- Recommendation Systems: Identifying similar items or users based on embedding vectors.
- AI-Powered Applications: Integrating LLM workflows with structured data using embeddings.
Creating a vector index significantly improves read performance for similarity queries, and it supports SQL semantics with WHERE clauses and LIMIT for post-filtering. With native vector data types (VECTOR(N)) and integrated indexing, MariaDB simplifies the development of applications requiring both relational and vector data processing.
How MinervaDB Can Help Customers Develop Vector Models and LLM Applications
MinervaDB positions itself as a trusted partner for organizations seeking to harness the power of vector databases and artificial intelligence through specialized consulting and engineering services. Their expertise extends to developing robust infrastructure for vector models and Large Language Model (LLM) applications, providing the foundation for advanced AI capabilities.
Expertise in Vector Database Infrastructure
MinervaDB specializes in designing and implementing vector database solutions optimized for AI and machine learning workloads. They offer deep technical knowledge in platforms like Milvus, an open-source vector database critical for powering similarity search across massive datasets. This includes mastering vector index algorithms such as IVF and HNSW, which are essential for achieving optimal performance in vector similarity searches—a cornerstone of modern AI applications like recommendation systems and semantic search.
Their services cover the entire lifecycle of vector database deployment, from initial setup and sizing for peak performance to seamless migration strategies for adopting vector databases. By introducing specialized data types for high-dimensional numerical arrays, MinervaDB helps organizations efficiently store and process embeddings, ensuring flexible dimensionality, efficient memory use, and fast data operations.
Enabling LLM Applications with Vectorized Processing
A key area of MinervaDB’s proficiency is implementing vectorized query processing specifically for LLM applications on platforms like MySQL HeatWave. This integration allows businesses to leverage their existing relational data infrastructure to support AI-driven workflows, enabling capabilities such as semantic search and personalized recommendations. By optimizing the technical architecture for LLMs, MinervaDB ensures that organizations can efficiently process and retrieve relevant information based on vector similarity, enhancing the intelligence of their applications.
With a full-stack approach to database infrastructure engineering, MinervaDB provides enterprise-grade solutions for scalable, reliable, and secure AI/ML systems . Their modern infrastructure is infused with AI to support autonomous database management, from installation and configuration to tuning and troubleshooting, allowing customers to focus on innovation rather than operational complexity.