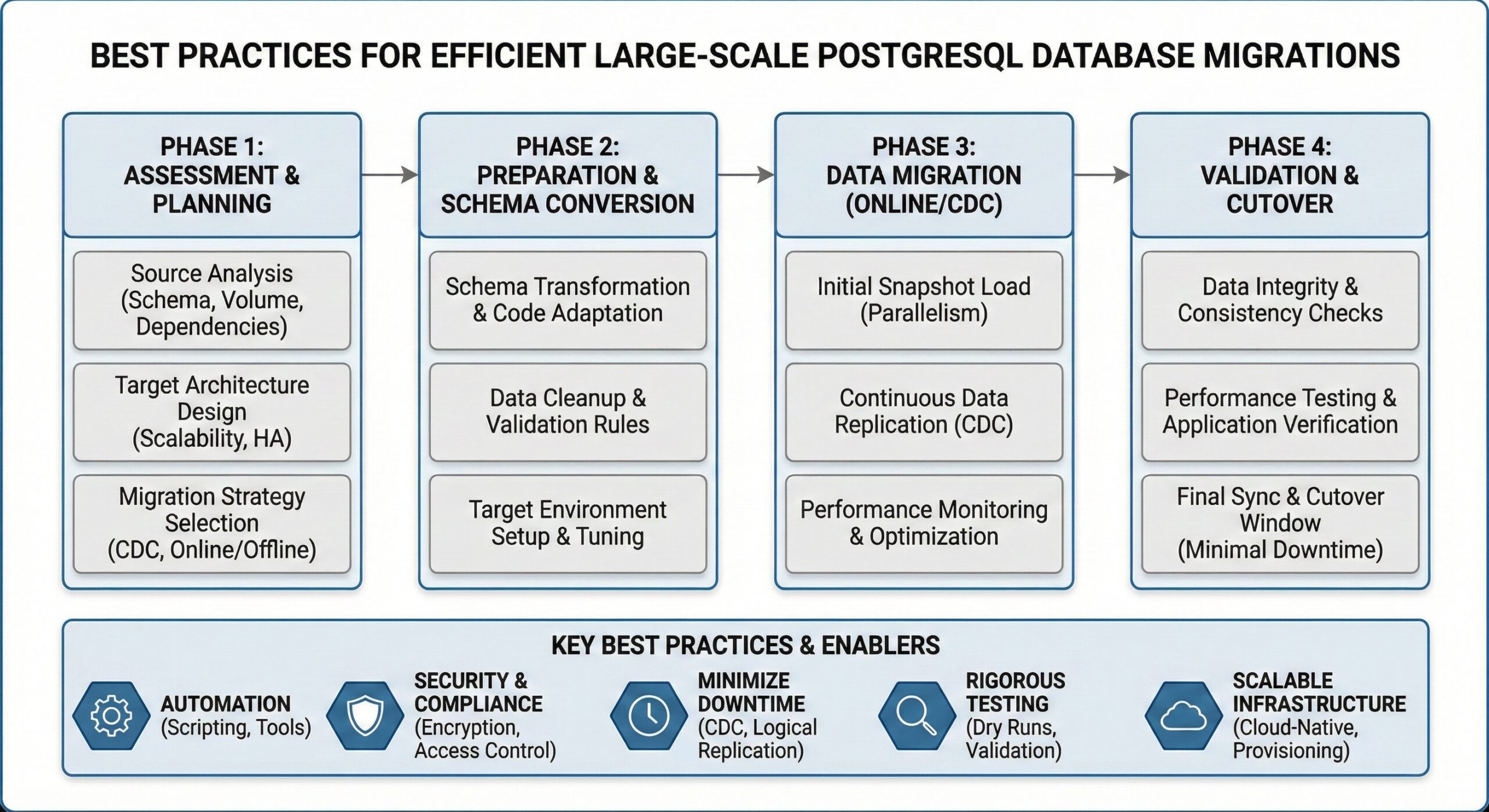
Best Practices for Efficient Large-Scale PostgreSQL Database Migrations
Large-scale PostgreSQL database migrations present unique challenges that require careful planning, advanced tooling, and strategic execution. As organizations scale to multi-terabyte and petabyte-scale datasets, traditional migration methods often fall short, leading to prolonged downtime and performance degradation. This comprehensive guide outlines proven strategies and best practices for executing efficient large-scale PostgreSQL migrations while minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity.
Understanding the Migration Landscape
Migrating multi-terabyte PostgreSQL databases requires balancing speed, data integrity, and system availability. Modern migration approaches have evolved beyond simple dump-and-restore methods to incorporate parallel processing, logical replication, and cloud-native solutions that can handle enterprise-scale workloads efficiently.
Pre-Migration Planning and Assessment
Database Size and Complexity Analysis
Before initiating any migration, conduct a thorough assessment of your database infrastructure. This includes:
- Total Data Volume: Understanding the complete size of your PostgreSQL database helps estimate migration time and infrastructure requirements
- Table Size Analysis: Large tables exceeding 100M rows may require special handling such as partitioning or parallel load techniques
- Schema Complexity: Identify dependencies, constraints, and custom functions that may impact migration strategy
- Performance Baseline: Establish current performance metrics to validate post-migration results
Infrastructure Requirements Assessment
Evaluate your current and target infrastructure capabilities, including:
- Network bandwidth and latency between source and destination
- Storage performance characteristics (IOPS, throughput)
- CPU and memory resources for parallel processing
- Backup and rollback strategies using LVM snapshots or ZFS clones
Advanced Migration Tools and Parallel Processing
Cloud Database Migration Service (DMS) MAXIMUM Mode
Modern cloud platforms offer optimized migration services that significantly outperform traditional methods. Google Cloud’s DMS MAXIMUM Mode demonstrates remarkable efficiency for 5TB+ datasets:
- Partitioned pglogical subscriptions: Divides tables into replication sets based on size thresholds (e.g., >50GB tables get dedicated workers)
- Zero-copy streaming: Achieves 95% bandwidth efficiency compared to 60-70% in traditional ETL pipelines
- Performance benchmarks: 8-12x faster than standard logical replication, completing 5TB migrations in 2.7 hours
Optimized pg_dump/pg_restore Parallelization
For physical server migrations, combine multi-threaded operations with storage optimizations:
# NVMe-optimized dump (40 vCPU environment) pg_dump -Fd -j 16 -Z 6 --compress=6 -f /nvme_backup mydb # Parallel restore with connection pooling pg_restore -j 24 -d newdb --no-privileges --no-owner /nvme_backup
Performance metrics: Achieve 2.8M rows/sec on AMD EPYC 7B13 with RAID-0 NVMe configuration.
Hybrid Migration Architecture
Different tools excel in specific scenarios:
| Tool | Parallelism | Throughput | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| PeerDB Streams | 16 workers | 1.2M rows/sec | Time-series data |
| pglogical | 8 workers | 650K rows/sec | Transactional tables |
| pg_dump | Single-thread | 200K rows/sec | Configuration tables |
Database Configuration Optimization
Source Database Tuning
Optimize your source database for migration workloads:
-- For 64GB RAM server ALTER SYSTEM SET shared_buffers = '38GB'; -- 60% of total RAM ALTER SYSTEM SET max_wal_senders = 20; -- Allow concurrent backups ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = 'logical'; -- Enable CDC replication SELECT pg_reload_conf();
Implementation Tip: Increase max_replication_slots to match parallel worker count plus 25% buffer.
Target Database Preparation
Configure the destination database for optimal ingestion performance:
-- Pre-migration setup ALTER SYSTEM SET max_parallel_workers = 32; ALTER SYSTEM SET max_worker_processes = 40; CREATE TABLESPACE ssd_vol1 LOCATION '/mnt/ebs_vol1'; ALTER DATABASE prod SET TABLESPACE ssd_vol1;
Critical Adjustment: Disable autovacuum during initial load (autovacuum = off) to prevent I/O contention.
Schema and Storage Optimization
Strategic Partitioning Implementation
For tables exceeding 100M rows, implement partitioning to improve query performance and enable parallel operations:
-- Time-based partitioning
CREATE TABLE sensor_data (
id BIGSERIAL,
recorded_at TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
payload JSONB
) PARTITION BY RANGE (recorded_at);
-- Monthly partitions
CREATE TABLE sensor_2024_06 PARTITION OF sensor_data
FOR VALUES FROM ('2024-06-01') TO ('2024-07-01')
TABLESPACE fast_ssd;
Migration Benefit: Enables parallel COPY operations per partition.
Index Optimization Strategies
Implement space-efficient indexing approaches:
-- BRIN for time-series (75% smaller than B-tree) CREATE INDEX readings_brin_idx ON sensor_data USING brin (recorded_at) WITH (pages_per_range=64); -- Concurrent index build CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY users_email_idx ON users(email);
Execution Strategy and Monitoring
Phased Migration Approach
Implement a structured migration process:
Schema Sync (0 Downtime):
pg_dump --schema-only -Fp source_db | psql target_db
Initial Data Load (48h for 10TB):
parallel -j 16 pg_dump -t {} | psql target_db ::: $(psql -Atqc "SELECT tablename FROM pg_tables")
CDC Replication (15min Cutover): Monitor replication lag using:
SELECT pid, client_addr, state,
pg_wal_lsn_diff(sent_lsn, write_lsn) AS send_lag,
pg_wal_lsn_diff(write_lsn, flush_lsn) AS write_lag
FROM pg_stat_replication;
Zero-Downtime Migration with Logical Replication
Logical replication enables near-zero downtime migrations by streaming data changes at the SQL level. This approach allows replication between different PostgreSQL versions and provides real-time data synchronization during the migration process.
Network Optimization for Cross-Cloud Migrations
For cross-cloud migrations, network tuning significantly enhances performance:
# AWS Direct Connect tuning sysctl -w net.core.rmem_max=2147483647 sysctl -w net.core.wmem_max=2147483647 iptables -t mangle -A POSTROUTING -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1440
Post-Migration Validation and Performance Benchmarking
Automated Consistency Checks
Implement comprehensive validation procedures:
# Schema checksum validation pg_dump --schema-only -Fp source | sha256sum > source.sha pg_dump --schema-only -Fp target | sha256sum > target.sha diff source.sha target.sha # Sample data verification psql source_db -c "SELECT * FROM transactions TABLESAMPLE BERNOULLI(0.01)" > source_sample.csv psql target_db -c "SELECT * FROM transactions TABLESAMPLE BERNOULLI(0.01)" > target_sample.csv cmp source_sample.csv target_sample.csv
Performance Analysis
Conduct thorough performance benchmarking post-migration:
EXPLAIN (ANALYZE, BUFFERS, VERBOSE) SELECT customer_id, SUM(amount) FROM partitioned_sales WHERE sale_date BETWEEN '2024-01-01' AND '2024-06-30' GROUP BY ROLLUP (customer_id);
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Avoiding Migration Mistakes
Common PostgreSQL migration mistakes include:
- Inadequate performance testing before production deployment
- Insufficient resource allocation for parallel operations
- Neglecting to optimize target database configuration
- Failing to implement proper monitoring and alerting
Memory Tuning Considerations
Set maintenance_work_mem = 1GB per restore job to prevent out-of-memory errors during parallel operations. For PostgreSQL 16 and later versions, leverage enhanced performance tuning parameters.
Real-World Implementation Example
Azure’s Flexible Server migration service demonstrates successful large-scale implementation:
- Hardware: 32 vCPU instances with 256GB RAM
- Parallelization: 8 parallel pglogical streams
- Performance: 7.5-hour migrations for 2TB financial databases
- Safety: ZFS snapshots for rollback capability
Conclusion and Best Practices Summary
Successful large-scale PostgreSQL migrations require a multi-faceted approach combining:
- Tool Parallelization: Leverage Cloud DMS or pglogical for partitioned streams
- Infrastructure Tuning: Optimize WAL, memory, and storage configurations
- Schema Design: Implement partitioning and space-efficient indexing
- Validation Automation: Use checksums and statistical sampling for verification
For mission-critical systems, conduct staged migrations following the Development → Stress Testing → Staging → Production workflow. Always maintain fallback options using LVM snapshots or ZFS clones, particularly when migrating datasets exceeding 1TB.
By implementing these proven strategies and leveraging modern migration tools, organizations can achieve efficient, reliable large-scale PostgreSQL migrations with minimal downtime and optimal performance outcomes. The key to success lies in thorough planning, appropriate tool selection, and systematic execution of the migration strategy tailored to your specific infrastructure and requirements.