Implementing Zero Trust in Snowflake: “Never Trust, Always Verify” at Every Level
In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data assets. The rise of cloud computing, remote work, and sophisticated cyber threats has necessitated a fundamental shift in how organizations approach data security. Enter Zero Trust architecture – a revolutionary security framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
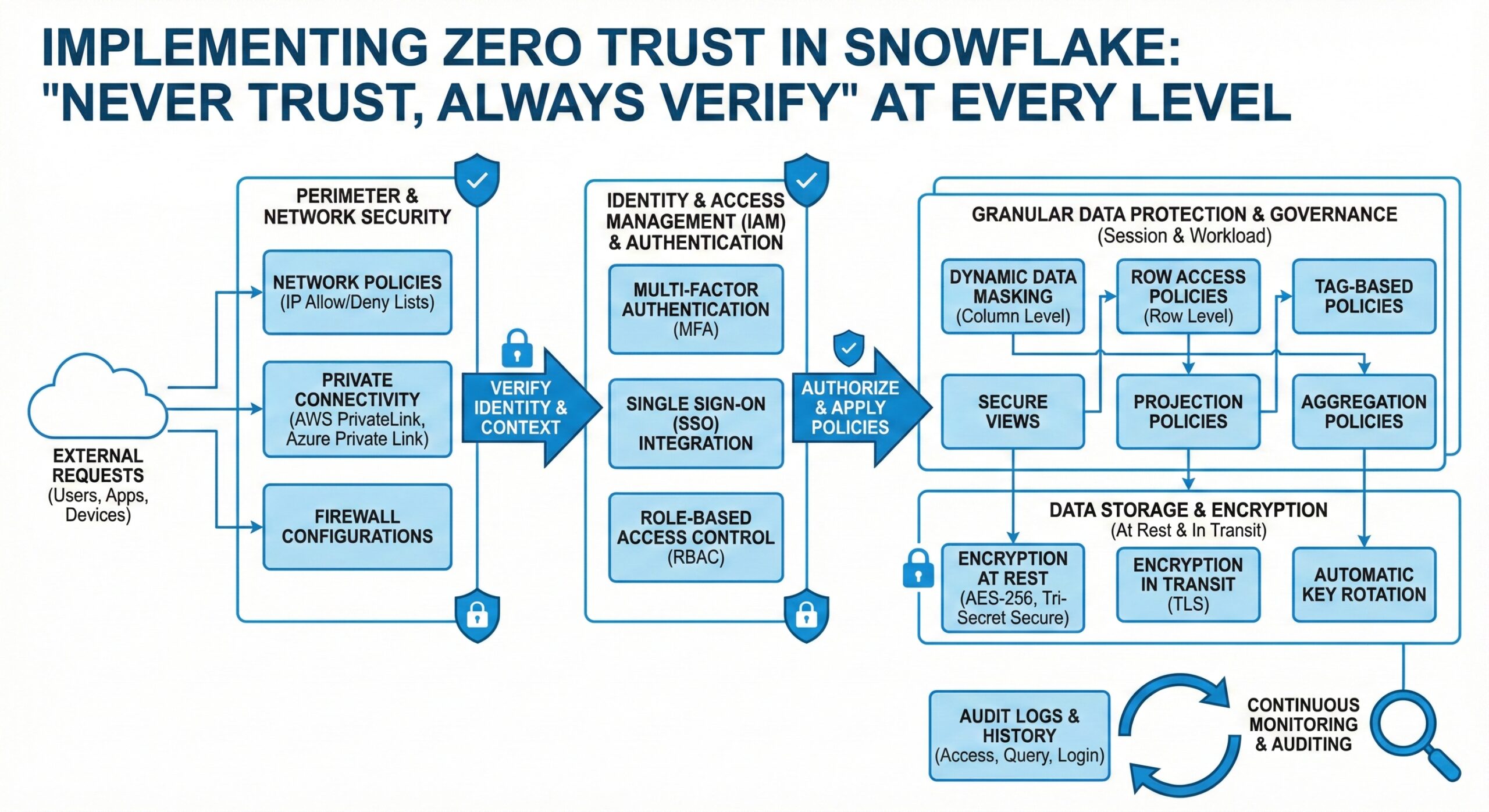
Snowflake, the leading cloud data platform, has embraced Zero Trust principles to provide comprehensive data protection across multiple layers of security. This article explores how Snowflake implements Zero Trust security controls at the row, column, session, and workload levels, enabling organizations to maintain robust data protection while ensuring seamless access for authorized users. Implementing Zero Trust in Snowflake is essential for modern data security.
Understanding Zero Trust: Beyond Traditional Security Models
Zero Trust represents a paradigm shift from the conventional “trust but verify” approach to a more stringent “never trust, always verify” methodology. This security model assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network perimeter, requiring continuous authentication and authorization for every user, device, and workload attempting to access data resources.
The core principles of Zero Trust include:
- Continuous verification: Every access request is authenticated and authorized
- Least privilege access: Users receive only the minimum permissions necessary
- Assume breach: Security controls operate under the assumption that threats may already be present
- Explicit verification: All access decisions are based on multiple data points and context
Snowflake’s Zero Trust Architecture: A Multi-Layered Approach
Snowflake’s implementation of Zero Trust architecture provides defense-in-depth security through multiple interconnected layers. The platform combines traditional access controls with advanced security features to create a comprehensive security framework that protects data at every level of interaction.
The Foundation: Strong Identity and Access Control
At the foundation of Snowflake’s Zero Trust implementation lies robust identity and access management. Organizations can integrate Snowflake with enterprise identity providers (IdPs) such as Okta, Azure AD, and others through Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities. This integration enables:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enforcement for all privileged roles
- Enterprise group mapping to Snowflake roles, eliminating reliance on built-in administrative roles for daily operations
- Layered role hierarchy implementation following organizational structure (ORG/ACCOUNT → functional roles → object roles)
- Least privilege principle application through granular permission management
Row-Level Security: Granular Data Access Control
Row-level security in Snowflake represents one of the most sophisticated implementations of Zero Trust at the data level. Through row access policies, organizations can implement dynamic, context-aware access controls that determine which rows of data users can access based on their identity, role, and other contextual factors.
How Row Access Policies Work
Snowflake creates dynamic secure views of database objects when row access policies are applied. The system evaluates policy expressions in real-time, binding column values to policy parameters and generating query outputs that contain only rows where the policy definition evaluates to TRUE.
Key features of row-level security include:
- Dynamic policy evaluation: Access decisions are made at query time based on current user context
- Mapping table integration: Policies can reference external mapping tables for complex access scenarios
- Multi-condition support: Policies can incorporate multiple criteria such as user roles, departments, geographic locations, and time-based restrictions
- Transparent implementation: Users experience seamless data access without awareness of underlying security controls
Implementation Best Practices
Effective row-level security implementation requires careful planning and design:
- Data classification: Identify sensitive data elements that require row-level protection
- Access pattern analysis: Understand how different user groups need to access data
- Policy design: Create policies that balance security requirements with operational efficiency
- Performance optimization: Design policies to minimize query performance impact
- Regular auditing: Monitor policy effectiveness and adjust as business requirements evolve
Column-Level Security: Protecting Sensitive Data Elements
Column-level security in Snowflake provides granular protection for sensitive data elements through Dynamic Data Masking and External Tokenization capabilities. This Zero Trust approach ensures that sensitive information is protected even when users have legitimate access to the underlying tables or views.
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic Data Masking represents a sophisticated approach to column-level protection that masks sensitive data at query time. This feature enables organizations to:
- Selectively mask data: Apply different masking rules based on user context and roles
- Maintain data utility: Preserve data format and structure while protecting sensitive values
- Support multiple masking functions: Implement various masking techniques including nullification, partial masking, and format-preserving encryption
- Enable conditional masking: Apply masking rules based on complex conditions and user attributes
External Tokenization
For organizations requiring the highest levels of data protection, Snowflake supports External Tokenization, which enables data to be tokenized before loading into the platform and detokenized at query runtime. This approach ensures that sensitive data never exists in plain text within the Snowflake environment.
Tag-Based Masking Policies
Snowflake’s tag-based masking policies provide scalable column-level security management. Organizations can:
- Apply consistent policies: Use tags to apply masking policies across multiple columns and tables
- Simplify management: Reduce administrative overhead through centralized policy management
- Ensure compliance: Maintain consistent data protection standards across the organization
- Support data governance: Integrate with broader data governance frameworks
Session-Level Security: Controlling User Interactions
Session-level security in Snowflake implements Zero Trust principles by continuously monitoring and controlling user sessions throughout their lifecycle. This approach ensures that user access remains secure and compliant with organizational policies.
Session Policies and Management
Snowflake’s session policies provide comprehensive control over user sessions, including:
- Session timeout controls: Automatic session termination after periods of inactivity
- Concurrent session limits: Restrictions on the number of simultaneous sessions per user
- Client application controls: Policies governing which client applications can establish sessions
- Geographic restrictions: Location-based session controls for enhanced security
Authentication Policies
Authentication policies in Snowflake enable organizations to implement sophisticated access controls that align with Zero Trust principles. These policies provide:
- Multi-method authentication: Support for various authentication mechanisms including SSO, key pairs, and OAuth
- Client-specific controls: Restrictions on which clients can authenticate using specific methods
- Security integration management: Controls over which security integrations can be used for authentication
- Conditional access: Context-aware authentication requirements based on user attributes and access patterns
Network Policies
Network policies represent a critical component of session-level security, enabling organizations to control network traffic and access patterns. Key capabilities include:
- IP address restrictions: Allow or deny access based on source IP addresses or ranges
- VPN integration: Support for VPN-based access controls
- Private connectivity: Integration with PrivateLink and other private connectivity solutions
- Egress controls: Management of outbound network traffic from Snowflake environments
Workload-Level Security: Isolating and Protecting Compute Resources
Workload-level security in Snowflake implements Zero Trust principles through comprehensive isolation and protection of compute resources. This multi-layered approach ensures that different workloads remain secure and isolated from each other while maintaining optimal performance.
Virtual Warehouse Isolation
Snowflake’s virtual warehouses provide robust security and performance isolation for different workloads. The platform implements multiple layers of isolation:
- Compute isolation: Each virtual warehouse operates as an independent compute cluster
- Resource segregation: Workloads cannot interfere with each other’s compute resources
- Security boundaries: Strong isolation prevents unauthorized access between workloads
- Performance guarantees: Dedicated resources ensure consistent performance for critical workloads
Workload Identity Federation
Workload Identity Federation represents an advanced Zero Trust capability that enables workloads to authenticate to Snowflake without managing long-lived credentials. This approach provides:
- Credential-less authentication: Eliminates the need to store and manage static credentials
- Identity provider integration: Seamless integration with cloud identity providers
- Automated credential rotation: Dynamic credential management reduces security risks
- Simplified implementation: Easier deployment compared to traditional authentication methods
Best Practices for Workload Security
Effective workload-level security implementation requires:
- Workload classification: Categorize workloads based on sensitivity and requirements
- Dedicated warehouses: Create separate virtual warehouses for different workload types
- Resource sizing: Appropriately size warehouses based on workload characteristics
- Access controls: Implement role-based access controls for warehouse usage
- Monitoring and auditing: Continuously monitor workload performance and security
Network and Device Controls: Securing the Perimeter
Snowflake’s Zero Trust implementation extends to comprehensive network and device controls that secure access from various endpoints and network locations.
Private Connectivity Options
Organizations can implement private connectivity through:
- AWS PrivateLink: Secure, private connectivity to Snowflake from AWS environments
- Azure Private Link: Private connectivity for Azure-based deployments
- Google Cloud Private Service Connect: Secure connectivity for Google Cloud Platform users
Machine-to-Machine Authentication
For automated systems and applications, Snowflake provides secure authentication options:
- Key pair authentication: RSA key-based authentication for service accounts
- OAuth integration: Secure token-based authentication with tightly scoped permissions
- Service account management: Dedicated account types for non-human access
Data-Centric Protection: Comprehensive Data Security
The data-centric protection layer of Snowflake’s Zero Trust architecture focuses on protecting data throughout its lifecycle.
Data Classification and Segmentation
Effective data protection begins with proper classification and segmentation:
- Sensitivity classification: Categorize data based on sensitivity levels (PII, PHI, financial, internal)
- Database segmentation: Separate sensitive data into dedicated databases and schemas
- Role-based access: Assign dedicated roles for different data categories
- Compliance alignment: Ensure data handling meets regulatory requirements
Time Travel and Fail-Safe
Snowflake’s Time Travel and Fail-safe features support Zero Trust principles by providing:
- Data recovery capabilities: Protection against accidental or malicious data changes
- Forensic analysis: Historical data access for security investigations
- Compliance support: Data retention capabilities for regulatory requirements
- Audit trails: Comprehensive logging of data access and modifications
Implementation Strategy: Building Zero Trust in Snowflake
Successfully implementing Zero Trust in Snowflake requires a systematic approach that addresses organizational, technical, and operational considerations.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
- Current state analysis: Evaluate existing security controls and identify gaps
- Risk assessment: Identify critical data assets and potential threat vectors
- Stakeholder engagement: Involve security, data, and business teams in planning
- Compliance mapping: Align implementation with regulatory requirements
Phase 2: Foundation Setup
- Identity integration: Implement SSO and MFA with enterprise identity providers
- Network policies: Establish baseline network access controls
- Role hierarchy: Design and implement organizational role structure
- Basic monitoring: Deploy fundamental logging and monitoring capabilities
Phase 3: Data Protection Implementation
- Data classification: Implement comprehensive data classification schemes
- Row-level policies: Deploy row access policies for sensitive data
- Column masking: Implement dynamic data masking for PII and sensitive elements
- Workload isolation: Establish dedicated virtual warehouses for different workload types
Phase 4: Advanced Controls and Optimization
- Advanced authentication: Implement workload identity federation and advanced authentication policies
- Fine-tuning: Optimize policies based on usage patterns and performance requirements
- Automation: Implement automated policy management and compliance monitoring
- Continuous improvement: Establish processes for ongoing security enhancement
Benefits of Zero Trust Implementation in Snowflake
Organizations implementing Zero Trust architecture in Snowflake realize significant benefits across multiple dimensions:
Enhanced Security Posture
- Reduced attack surface: Granular access controls minimize potential exposure
- Improved threat detection: Continuous monitoring enables rapid threat identification
- Compliance assurance: Comprehensive controls support regulatory compliance
- Data breach prevention: Multi-layered protection reduces breach risk and impact
Operational Efficiency
- Simplified access management: Centralized policies reduce administrative overhead
- Automated compliance: Built-in controls support automated compliance reporting
- Reduced manual processes: Policy-driven access reduces manual intervention requirements
- Improved audit capabilities: Comprehensive logging supports efficient auditing
Business Enablement
- Secure data sharing: Confident data sharing with internal and external partners
- Accelerated analytics: Secure access to data enables faster business insights
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting compliance requirements enables business expansion
- Risk mitigation: Reduced security risks support business growth initiatives
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Zero Trust implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement.
Key Metrics and KPIs
Organizations should track:
- Access pattern analysis: Monitor user access patterns for anomalies
- Policy effectiveness: Measure the effectiveness of security policies
- Performance impact: Monitor the performance impact of security controls
- Compliance metrics: Track compliance with regulatory requirements
Regular Assessment and Updates
- Quarterly reviews: Regular assessment of security policies and controls
- Threat landscape monitoring: Stay current with emerging threats and vulnerabilities
- Technology updates: Leverage new Snowflake security features as they become available
- User feedback: Incorporate user feedback to optimize security and usability balance
Conclusion: Embracing Zero Trust for Data Security Excellence
Implementing Zero Trust architecture in Snowflake represents a fundamental shift toward more secure, resilient, and compliant data management. By applying the “never trust, always verify” principle at the row, column, session, and workload levels, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of data protection while maintaining the flexibility and performance required for modern analytics and data science initiatives.
The comprehensive security controls available in Snowflake enable organizations to implement sophisticated Zero Trust architectures that protect against both external threats and insider risks. From granular row-level access policies to advanced workload identity federation, Snowflake provides the tools necessary to build and maintain a robust security posture.
As cyber threats continue to evolve and regulatory requirements become more stringent, Zero Trust architecture in Snowflake positions organizations for long-term success. The investment in comprehensive data security not only protects valuable data assets but also enables confident data sharing, accelerated analytics, and sustainable business growth.
Organizations embarking on their Zero Trust journey with Snowflake should approach implementation systematically, starting with strong foundations and gradually building more sophisticated controls. With proper planning, implementation, and ongoing management, Zero Trust architecture in Snowflake delivers both immediate security benefits and long-term strategic value for data-driven organizations.
Further Reading
- Data Warehousing and Data Lakes Engineering with MinervaDB
- Cut Snowflake Spend by 30% in 90 Days
- Optimizing Query Performance in Snowflake
- From Chaos to Clarity – Case Study of a Failed CDP Implementation
- PostgreSQL 18 Performance Tuning