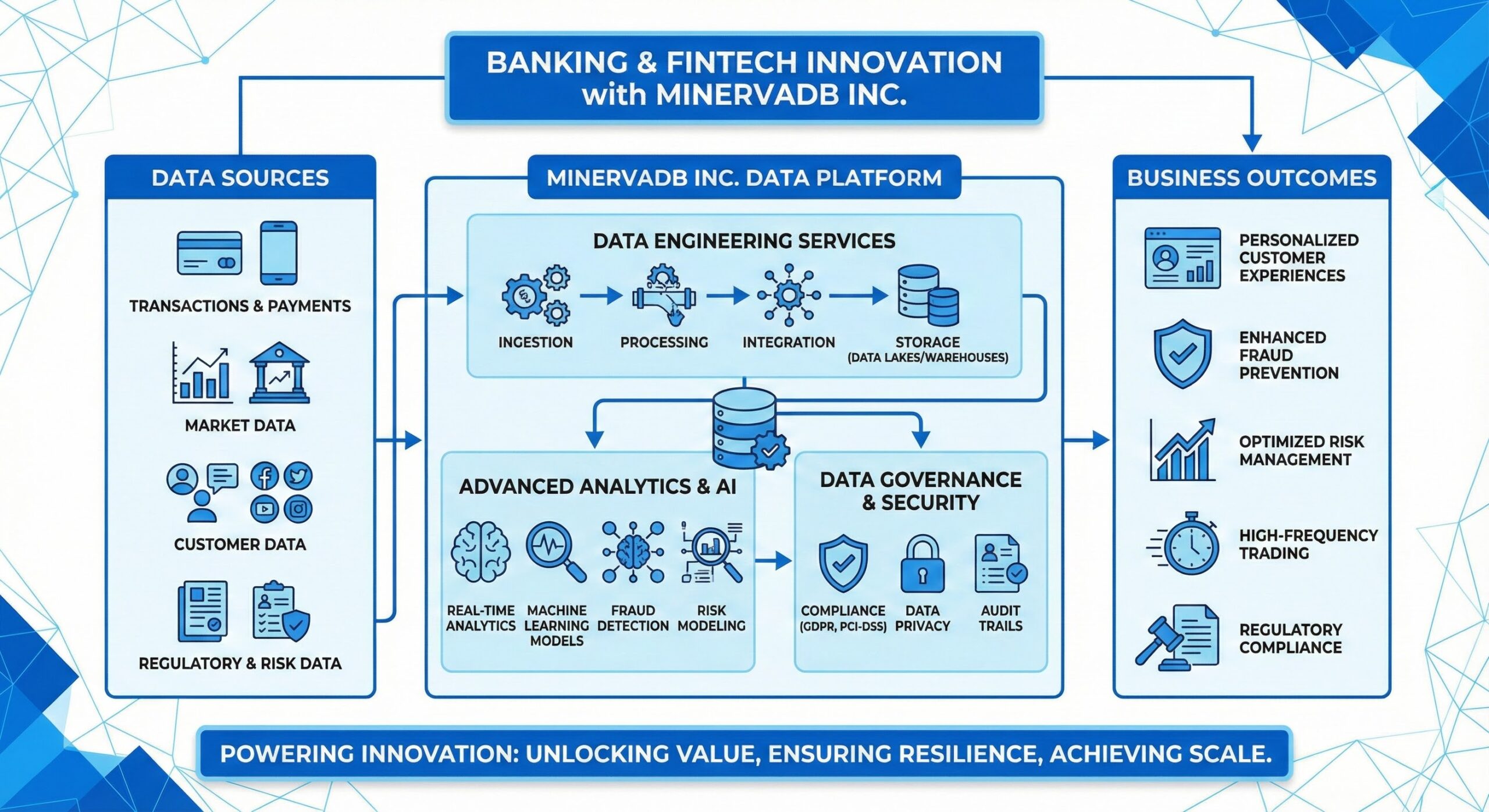
Data Engineering and Analytics in Banking and FinTech: Powering Innovation with MinervaDB Inc.
The financial services landscape is undergoing a seismic transformation driven by digital disruption, regulatory complexity, and evolving customer expectations. Banks and FinTech companies are no longer just competing on products—they’re competing on data. The ability to collect, process, analyze, and act upon vast volumes of structured and unstructured data in real time has become a critical differentiator. In this environment, robust data engineering and analytics infrastructure is not merely an enabler—it’s a strategic imperative.
MinervaDB Inc. stands at the forefront of this revolution, delivering cutting-edge data solutions tailored specifically for the unique demands of the banking and financial technology sectors. From high-frequency trading platforms to fraud detection systems, personalized customer experiences to risk modeling, MinervaDB’s comprehensive suite of data engineering services empowers institutions to unlock the full value of their data assets while ensuring compliance, resilience, and performance at scale.
The Data Challenge in Modern Financial Services
Financial institutions today operate in one of the most data-intensive industries in the world. Every transaction, customer interaction, market movement, and compliance event generates data that must be captured, stored, processed, and analyzed. Legacy systems, often built on monolithic architectures and relational databases, struggle to keep pace with the velocity, variety, and volume of modern data workloads.
Banks face increasing pressure to deliver seamless omnichannel experiences, detect fraudulent activity in real time, comply with stringent regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and PSD2, and leverage advanced analytics for credit scoring, portfolio management, and algorithmic trading. Meanwhile, FinTech startups disrupt traditional models with agile, data-driven platforms that offer faster onboarding, lower fees, and hyper-personalized services.
To thrive in this environment, organizations need a modern data architecture that supports:
- Real-time processing for instant decision-making
- Horizontal scalability to handle unpredictable workloads
- High availability and fault tolerance to ensure continuous operations
- Strong security and governance to protect sensitive financial data
- Interoperability across hybrid and multi-cloud environments
MinervaDB Inc. addresses these challenges through a holistic approach to data engineering, combining deep expertise in distributed systems, cloud-native technologies, and domain-specific knowledge of financial services.
NoSQL Database Architecture and Operations
As financial applications evolve beyond simple CRUD operations to complex event-driven workflows, NoSQL databases have become essential components of modern data stacks. Their schema-flexible design, horizontal scalability, and high performance make them ideal for use cases such as user profiles, session stores, real-time analytics, and transaction logging.
MongoDB Enterprise Implementation
MongoDB has emerged as a leading document-oriented NoSQL database, widely adopted in both banking and FinTech for its flexibility, developer-friendly interface, and enterprise-grade capabilities. MinervaDB delivers comprehensive MongoDB solutions designed to meet the rigorous demands of financial institutions.
Sharding Strategies: Horizontal Scaling Across Distributed Clusters
One of the core strengths of MongoDB is its native support for sharding—partitioning large datasets across multiple servers to distribute read and write loads. This capability is crucial for financial applications that experience exponential data growth, such as digital wallets, payment gateways, and customer 360 platforms.
MinervaDB implements intelligent sharding strategies based on access patterns, data distribution, and query performance. By selecting appropriate shard keys—such as customer ID, account number, or geographic region—our engineers ensure even data distribution and minimize cross-shard queries that can degrade performance. We also employ zone sharding for regulatory compliance, allowing data residency controls that align with jurisdictional requirements.
For example, a global bank may use sharding to isolate customer data by region, ensuring GDPR compliance in Europe while maintaining low-latency access for local users. MinervaDB configures shard clusters with optimal replica set configurations, balancing throughput, consistency, and disaster recovery needs.
Replica Set Configuration: Automated Failover and Data Redundancy
High availability is non-negotiable in financial services. MinervaDB configures MongoDB replica sets with automated failover mechanisms that ensure continuous operation even during hardware failures or network outages.
A typical production deployment includes at least three members: a primary node handling writes and two secondaries replicating data asynchronously. In the event of a primary failure, an automatic election process promotes a secondary to primary within seconds, minimizing downtime. MinervaDB also recommends arbiters for odd-numbered topologies and hidden or delayed members for backup and auditing purposes.
We implement oplog monitoring and replication lag alerts to proactively detect issues before they impact service levels. Additionally, we configure read preferences to route analytical queries to secondaries, offloading the primary and improving overall system responsiveness.
Performance Optimization: Index Optimization, Aggregation Pipeline Tuning
Efficient querying is essential for responsive applications. MinervaDB conducts thorough performance assessments to identify slow queries and optimize indexing strategies. We leverage compound indexes, partial indexes, and TTL indexes where appropriate to reduce storage overhead and improve query speed.
The MongoDB aggregation pipeline is a powerful tool for transforming and analyzing data within the database. MinervaDB fine-tunes aggregation stages to minimize memory usage, avoid blocking operations, and utilize indexes effectively. For instance, in a fraud detection pipeline, we might optimize stages that filter transactions by amount, location, and velocity before joining with user behavior profiles.
Our team uses MongoDB’s explain plans and performance schema to benchmark improvements and validate tuning efforts. We also integrate with APM tools to monitor query performance in production and recommend adjustments based on actual usage patterns.
Security Implementation: Authentication, Authorization, and Encryption Protocols
Security is paramount when dealing with financial data. MinervaDB implements a defense-in-depth strategy for MongoDB security, including:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with custom roles aligned to job functions
- LDAP and Active Directory integration for centralized identity management
- TLS/SSL encryption for data in transit
- Field-level encryption for sensitive attributes like account numbers and PII
- Audit logging enabled to track all administrative and data access activities
We follow MongoDB’s security checklist rigorously, disabling unnecessary features, enforcing strong password policies, and configuring firewalls to restrict access to trusted IPs. For cloud deployments, we integrate with IAM policies and VPC peering to further tighten security boundaries.
Cassandra Distributed Systems
Apache Cassandra is another cornerstone of MinervaDB’s NoSQL offerings, particularly suited for write-heavy, globally distributed applications. Its decentralized architecture, linear scalability, and tunable consistency model make it ideal for time-series data, audit logs, messaging systems, and high-throughput transaction processing.
Multi-Datacenter Deployment: Global Distribution with Eventual Consistency
Cassandra excels in multi-datacenter deployments, enabling banks and FinTechs to build resilient, low-latency systems across geographies. MinervaDB designs Cassandra clusters with replication across multiple availability zones and regions, ensuring data durability and availability even during regional outages.
Using NetworkTopologyStrategy, we configure replication factors per datacenter to balance consistency and performance. For example, a FinTech serving customers in North America and Europe might deploy clusters in US-East, US-West, and EU-West, with RF=3 in each region and synchronous replication within regions but asynchronous between them.
This architecture supports eventual consistency, which is acceptable for many financial use cases such as activity feeds, balance updates, and notification queues. MinervaDB also implements conflict resolution strategies using timestamps or application-level logic to maintain data integrity.
Performance Tuning: Compaction Strategies, Memory Optimization, and Read/Write Path Optimization
Cassandra’s performance hinges on proper tuning of its internal components. MinervaDB optimizes compaction strategies—such as Size-Tiered, Leveled, and Time-Window Compaction—based on data access patterns. For time-series data like stock ticks or transaction logs, we often recommend Time-Window Compaction to improve delete efficiency and reduce tombstone overhead.
Memory settings, including heap size, cache sizes, and off-heap allocation, are tuned to maximize throughput and minimize GC pauses. We analyze SSTable patterns and adjust flush thresholds to prevent bottlenecks.
On the read path, MinervaDB leverages Bloom filters, row caches, and partition key design to reduce disk I/O. On the write path, we ensure proper batching and leverage Cassandra’s append-only storage engine to achieve sustained high write throughput—critical for real-time transaction processing.
Capacity Planning: Node Sizing, Cluster Expansion, and Resource Allocation
Proper capacity planning prevents performance degradation and unplanned downtime. MinervaDB performs detailed workload analysis to determine optimal node sizing based on CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network bandwidth requirements.
We use predictive modeling to forecast growth and plan cluster expansions well in advance. Rolling upgrades and incremental scaling allow us to add nodes without service interruption. Our engineers monitor key metrics such as load per node, replication latency, and repair times to ensure cluster health.
For financial institutions, we also incorporate compliance and audit requirements into capacity planning, ensuring sufficient resources for logging, monitoring, and forensic analysis.
Operational Excellence: Monitoring, Backup Strategies, and Disaster Recovery
MinervaDB implements comprehensive operational practices to ensure Cassandra clusters run smoothly in production. We deploy monitoring solutions using Prometheus and Grafana to visualize key performance indicators, set up alerting for anomalies, and conduct regular health checks.
Backup strategies include incremental snapshots and incremental repairs using tools like Medusa or custom scripts integrated with object storage. Point-in-time recovery capabilities are tested regularly to validate disaster recovery readiness.
We also automate routine tasks such as repairs, compactions, and upgrades using orchestration tools, reducing manual intervention and human error.
Redis and Valkey In-Memory Solutions
In-memory data stores play a vital role in accelerating application performance, especially in latency-sensitive financial applications. Redis—and its recently forked successor, Valkey—offer sub-millisecond response times, making them ideal for caching, session management, rate limiting, and real-time analytics.
High-Performance Caching: Application-Level Caching Strategies and Session Management
MinervaDB deploys Redis/Valkey as a high-performance caching layer between applications and backend databases. This reduces load on primary systems, improves response times, and lowers operational costs.
We implement intelligent caching strategies such as:
- Cache-aside (lazy loading): Data is loaded into the cache only when requested
- Write-through: Updates are written to both cache and database simultaneously
- Write-behind: Writes go to cache first, then asynchronously to the database
For online banking portals and mobile apps, we use Redis to store user sessions, enabling fast authentication and personalized dashboards. Session data is encrypted and TTL-managed to enhance security and resource efficiency.
Data Structure Optimization: Efficient Use of Redis Data Types for Specific Use Cases
Redis offers rich data structures—including strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, and streams—that can be leveraged for domain-specific problems. MinervaDB selects the optimal data type based on use case requirements.
For example:
- Sorted sets are used for leaderboards in gamified savings apps
- Streams power real-time transaction feeds and event sourcing architectures
- HyperLogLog enables approximate counting of unique users or transactions with minimal memory
- Geospatial indexes support location-based services like branch finders or ATM locators
In fraud detection systems, we use Redis to maintain real-time counters of transaction frequency, velocity, and geolocation anomalies, enabling immediate blocking of suspicious activity.
Clustering and Replication: Redis Cluster Setup and Master-Slave Configurations
To ensure scalability and high availability, MinervaDB configures Redis in clustered mode with sharding and automatic failover. The Redis Cluster architecture distributes data across multiple nodes using hash slots, allowing linear scaling up to thousands of nodes.
We implement master-slave replication with Sentinel or Raft-based consensus for automatic failover. Replicas serve read-heavy workloads, enabling read scaling while maintaining consistency.
For mission-critical applications, we recommend active-active geo-replication using third-party tools or cloud-managed services to provide disaster recovery across regions.
Memory Management: Optimization Strategies for Large-Scale Deployments
Memory is the primary constraint in Redis deployments. MinervaDB employs several strategies to optimize memory usage:
- Key expiration policies to automatically remove stale data
- Memory fragmentation reduction through proper allocation tuning
- Data compression techniques for large values
- Eviction policies such as LRU, LFU, or TTL-based removal under memory pressure
We also conduct regular memory profiling to identify memory hogs and refactor inefficient data models. For large-scale deployments, we recommend Redis Enterprise or cloud-managed offerings that provide enhanced memory efficiency and multi-tenancy support.
NewSQL and Modern Database Platforms
While NoSQL databases excel in scalability and flexibility, many financial applications still require the strong consistency, ACID transactions, and SQL interface provided by relational systems. NewSQL databases bridge this gap, offering the scalability of NoSQL with the transactional guarantees of traditional RDBMS.
ClickHouse Analytics Infrastructure
ClickHouse has emerged as a leading OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) database, renowned for its lightning-fast query performance on large datasets. MinervaDB leverages ClickHouse for real-time analytics, business intelligence, and data warehousing in financial services.
Real-Time Analytics: OLAP Query Optimization for Large-Scale Data Processing
ClickHouse’s columnar storage engine and vectorized query execution enable it to process billions of rows in seconds. MinervaDB optimizes schema design using MergeTree engines, choosing appropriate primary keys and partitioning strategies to accelerate filtering and aggregation.
For example, in a credit card analytics platform, we might partition data by month and sort by customer ID and transaction timestamp, enabling fast roll-ups for spending patterns, merchant categorization, and anomaly detection.
We also leverage materialized views and pre-aggregated tables to speed up common queries, reducing computational overhead at query time.
Distributed Architecture: Multi-Node Cluster Configuration and Management
MinervaDB deploys ClickHouse in distributed mode using ZooKeeper or ClickHouse Keeper for coordination. Data is replicated across nodes for fault tolerance and sharded for horizontal scaling.
We configure distributed tables that abstract the underlying sharding, allowing applications to query data seamlessly across the cluster. Our engineers tune replication settings, background merges, and part management to maintain optimal performance.
Data Ingestion: High-Throughput Data Loading and ETL Pipeline Optimization
Financial data pipelines often involve ingesting millions of transactions per minute. MinervaDB builds high-throughput ingestion pipelines using Kafka, Flink, or Spark Streaming to feed data into ClickHouse.
We batch inserts efficiently, manage mutations carefully, and monitor ingestion lag to ensure data freshness. For streaming use cases, we integrate ClickHouse with materialized views over Kafka topics, enabling real-time dashboards and alerting.
Performance Tuning: Query Optimization and Resource Allocation Strategies
MinervaDB conducts query profiling to identify bottlenecks, rewrite inefficient queries, and recommend indexing or schema changes. We tune server settings such as max_threads, memory limits, and disk I/O priorities to match workload characteristics.
Cost-based optimization and query caching further enhance performance, especially for recurring reports and dashboards used by risk, compliance, and marketing teams.
Trino Query Engine Optimization
Trino (formerly PrestoSQL) is a distributed SQL query engine that enables federated querying across disparate data sources. MinervaDB uses Trino to unify access to data stored in data lakes, warehouses, and operational databases, eliminating data silos.
Federated Query Processing: Cross-Platform Data Access and Integration
With Trino, financial analysts can run SQL queries that join data from MySQL, PostgreSQL, Kafka, Hive, S3, and even MongoDB or Cassandra through connectors. This eliminates the need for complex ETL pipelines just to answer ad-hoc questions.
MinervaDB configures and optimizes Trino catalogs for various data sources, ensuring secure, low-latency access. We implement view layers to abstract complexity and provide governed access to business users.
Performance Optimization: Query Planning, Resource Management, and Caching Strategies
Trino’s cost-based optimizer generates efficient execution plans. MinervaDB tunes session properties, splits, and task concurrency to maximize parallelism and reduce query latency.
We deploy coordinator high availability setups and scale worker nodes dynamically based on workload. Result caching is enabled for frequent queries, reducing redundant computation.
Security Implementation: Authentication, Authorization, and Data Governance
MinervaDB integrates Trino with LDAP, Kerberos, or OAuth for authentication. Row-level and column-level security policies are enforced using system access controls and custom plugins.
Audit logging captures all queries for compliance and forensic analysis. We also integrate with data governance platforms like Apache Atlas to track data lineage and classification.
Connector Configuration: Integration with Diverse Data Sources and Formats
MinervaDB configures and extends Trino connectors to support various formats including Parquet, ORC, Avro, JSON, and CSV. We optimize connector settings for performance, such as pushdown predicates, projection pruning, and split generation.
For real-time analytics, we enable Kafka connectors with JSON or Avro deserializers to query streaming topics directly.
Cloud-Native Database Infrastructure
The shift to cloud computing has transformed how databases are provisioned, managed, and scaled. MinervaDB provides end-to-end cloud-native database services across major public clouds, enabling financial institutions to achieve agility, resilience, and cost efficiency.
Multi-Cloud Database Management
Avoiding vendor lock-in and ensuring business continuity are top priorities for banks. MinervaDB designs multi-cloud database strategies that leverage the strengths of AWS, Azure, and GCP while maintaining operational consistency.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of managed database services. MinervaDB optimizes their usage for financial workloads:
- Amazon RDS: We manage MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server instances with automated backups, patching, and read replicas. Parameter group tuning and performance insights help maintain optimal performance.
- Amazon Aurora: For high-performance OLTP workloads, we deploy Aurora with serverless options for unpredictable traffic or provisioned clusters for steady-state workloads. Global databases enable cross-region replication with sub-second latency.
- Amazon Redshift: As a petabyte-scale data warehouse, Redshift is optimized for complex analytics. MinervaDB tunes sort keys, distribution styles, and vacuum processes to maintain query performance. We integrate with ML-based forecasting for capacity planning.
- DocumentDB: For MongoDB workloads on AWS, DocumentDB provides managed compatibility. We assess trade-offs between DocumentDB and self-managed MongoDB on EC2, recommending based on feature needs and cost.
Microsoft Azure
Azure’s integrated ecosystem is ideal for enterprises with existing Microsoft investments:
- Azure SQL Database: We configure auto-tuning, threat detection, and advanced data security features. Hyperscale edition is recommended for large databases requiring fast scaling.
- Azure Cosmos DB: This globally distributed, multi-model database supports document, key-value, graph, and columnar data. MinervaDB designs partitioning strategies and selects consistency levels (from strong to eventual) based on application needs.
- Azure Synapse Analytics: Combining data integration, enterprise data warehousing, and big data analytics, Synapse is optimized for hybrid workloads. We build pipelines using Spark pools and SQL on-demand for flexible processing.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP emphasizes data analytics and AI/ML integration:
- Google BigQuery: A serverless, highly scalable data warehouse that uses SQL. MinervaDB optimizes queries, manages partitioned and clustered tables, and leverages BigQuery ML for predictive analytics without moving data.
- Cloud SQL: Managed MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server instances with high availability and replication options. We integrate with VPC Service Controls for enhanced security.
- Cloud Spanner: A globally consistent, horizontally scalable relational database. MinervaDB uses it for mission-critical applications requiring strong consistency across regions, such as core banking ledgers.
Specialized Platforms
Beyond general-purpose databases, MinervaDB supports specialized platforms that address niche but critical use cases.
Snowflake: Data Cloud Optimization and Performance Tuning
Snowflake’s separation of compute and storage enables elastic scaling. MinervaDB configures virtual warehouses for different workloads (ETL, reporting, analytics), implements time travel and cloning for testing, and optimizes clustering keys for query performance.
We also integrate Snowflake with data sharing platforms, enabling secure data exchange between banks, regulators, and partners.
Databricks: Unified Analytics Platform Configuration and Optimization
Built on Apache Spark, Databricks unifies data engineering, data science, and machine learning. MinervaDB sets up Delta Lake for ACID transactions on data lakes, configures autoscaling clusters, and optimizes Spark jobs for ETL and ML pipelines.
Notebooks and workflows are version-controlled and CI/CD integrated for reproducibility. We enable Unity Catalog for data governance and lineage tracking.
Oracle MySQL HeatWave: In-Memory Analytics Acceleration
MySQL HeatWave combines OLTP and OLAP in a single engine, eliminating the need for ETL to a separate analytics database. MinervaDB activates HeatWave clusters linked to MySQL DB systems, enabling real-time analytics on transactional data.
We optimize heatwave loading, monitor query offload ratios, and tune memory settings to maximize performance gains for reporting and dashboarding.
Conclusion
In the fast-evolving world of banking and FinTech, data is the new currency. The ability to harness this data—quickly, securely, and intelligently—determines competitive advantage. MinervaDB Inc. empowers financial institutions with a comprehensive, future-ready data engineering and analytics platform that combines the best of NoSQL, NewSQL, in-memory, and cloud-native technologies.
From MongoDB and Cassandra to ClickHouse and Trino, from AWS and Azure to Snowflake and Databricks, MinervaDB delivers tailored solutions that address the full spectrum of data challenges. Our expertise in performance tuning, security, scalability, and operational excellence ensures that clients not only deploy cutting-edge technology but also derive maximum business value from it.
As artificial intelligence, real-time decisioning, and open banking continue to reshape the industry, MinervaDB remains committed to innovation, helping banks and FinTechs build resilient, agile, and intelligent data infrastructures for the future.