SQL Server Security, Data Privacy, and Data Security: A Comprehensive Guide from MinervaDB
At MinervaDB, we understand that protecting your SQL Server databases is not merely an IT requirement—it is a fundamental business imperative. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the security of SQL Server environments has become paramount. We have developed this comprehensive guide to help you implement robust security measures that protect your data assets while ensuring regulatory compliance and operational excellence.
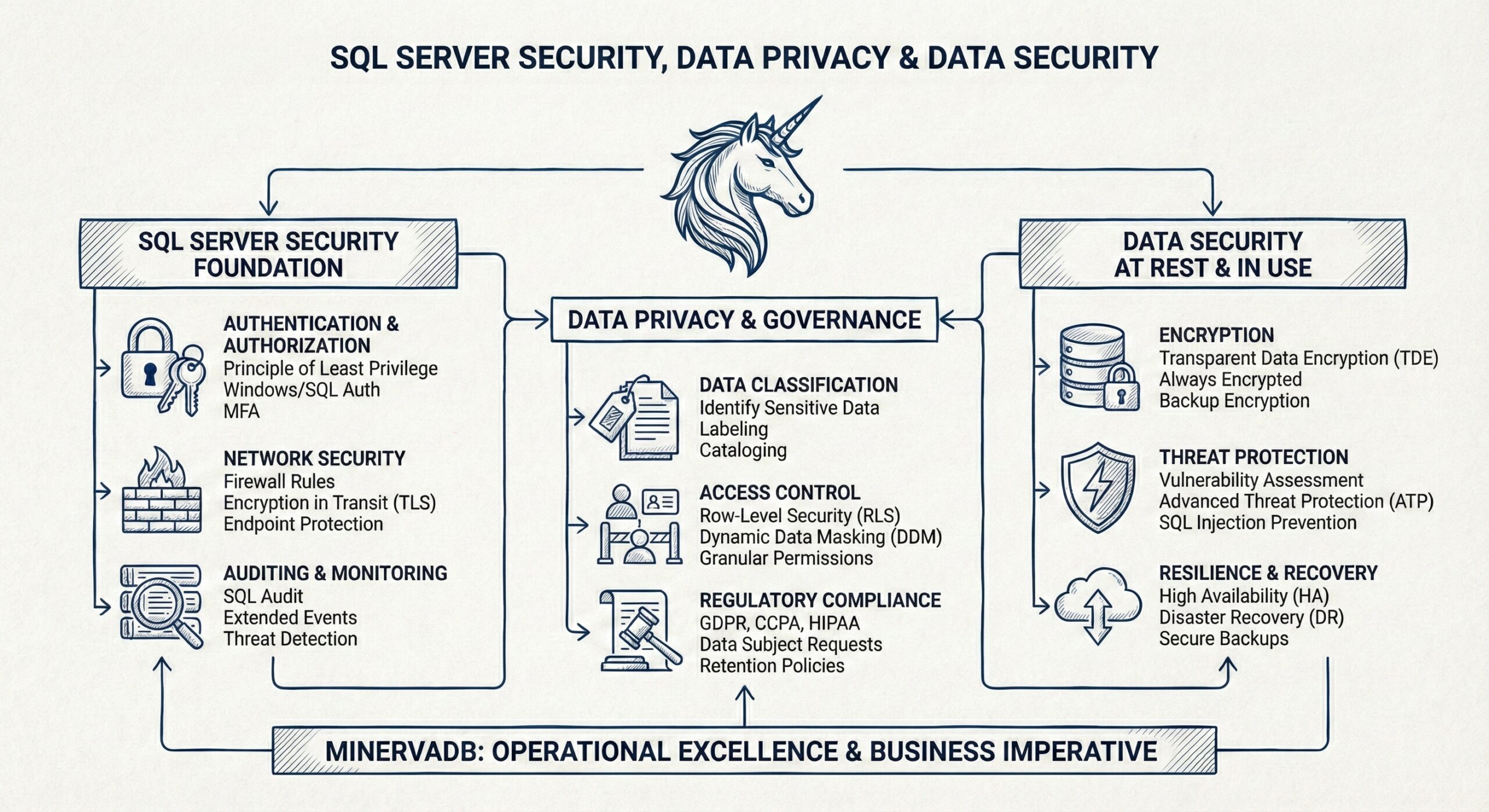
Understanding the Modern SQL Server Security Landscape
SQL Server security encompasses a wide array of measures designed to protect your database from unauthorized access and potential threats. At MinervaDB, we approach SQL Server security through a layered methodology that provides a defense-in-depth solution, using multiple security capabilities targeted at different security scopes . We believe that database security controls are mechanisms that enforce data protection policies within an organization, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential, integral, and available only to authorized users.
Modern database security controls have evolved to address sophisticated threats, demanding an intricate balance between accessibility and security. We recognize that these controls have become more intelligent, utilizing AI and machine learning to predict and preempt potential breaches. By analyzing vast amounts of data, advanced security systems can identify unusual patterns that may indicate a security threat, allowing your organization to act before a breach occurs.
Authentication and Authorization: The Foundation of SQL Server Security
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
We strongly advocate for multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a standard practice in SQL Server environments. MFA requires users to provide multiple pieces of evidence to verify identities, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised. At MinervaDB, we help organizations integrate MFA with single sign-on (SSO) systems, which streamlines the authentication process while allowing users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials.
We also recommend implementing adaptive authentication techniques that assess the risk level of each login attempt based on factors such as location, device, and time of access. This approach adjusts authentication requirements accordingly, enhancing security measures without compromising user convenience.
Role-Based Access Control Implementation
We implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure that users have access only to the information necessary for specific roles. This minimizes the risk of data exposure and limits potential damage in the event of a security breach. The principle of least privilege should guide the configuration of roles and permissions, ensuring minimal exposure of critical data.
At MinervaDB, we guide organizations in placing Active Directory users in AD groups, ensuring AD groups exist in SQL Server roles, and that SQL Server roles are granted the minimum permissions required by applications . We recommend choosing Active Directory over SQL Server authentication whenever possible, as it simplifies user management when employees leave the company or change roles.
Encryption: Protecting Data at Rest and in Transit
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Transparent Data Encryption protects data at the file level by providing encryption-at-rest to database files . TDE ensures that database files, backup files, and tempdb files cannot be attached and read without proper certificates decrypting database files. Without TDE, an attacker could potentially take physical media such as drives or backup tapes and restore or attach the database to read the contents.
We implement TDE to perform real-time I/O encryption and decryption of data and log files. The encryption uses a database encryption key (DEK) that is stored in the database boot record for availability during recovery. The DEK is a symmetric key secured by using a certificate stored in the master database of the server or an asymmetric key protected by an Extensible Key Management module.
At MinervaDB, we recognize that TDE has become widespread due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Organizations appreciate the ability to protect data without requiring significant changes to applications or infrastructure. We often implement TDE in conjunction with other encryption techniques to provide layered security, using TDE to protect data at rest while employing column-level encryption to protect sensitive data fields.
Always Encrypted for End-to-End Protection
We implement Always Encrypted to encrypt data at rest and over the wire, with encrypted data only decrypted by client libraries at the application client level . This feature is essential for protecting sensitive data such as credit card numbers or social security numbers within SQL Server environments.
Always Encrypted provides end-to-end encryption, ensuring that data remains protected from the moment it is created until it is no longer needed. This approach provides a high level of security, as data is never exposed in plaintext form, even within the database. We recommend using randomized encryption over deterministic where possible, and Always Encrypted with secure enclaves can improve performance for comparison operations such as BETWEEN, IN, LIKE, DISTINCT, and Joins .
Column-Level Encryption Strategies
We also implement column-level encryption to protect specific columns within a database, providing targeted protection for sensitive information. By encrypting only the necessary data, organizations can minimize the performance impact of encryption while ensuring applications remain responsive and efficient.
At MinervaDB, we help organizations grant permissions at the column level to tables, views, or table-valued functions . We note that only SELECT, REFERENCES, and UPDATE permissions can be granted on a column, and that a table-level DENY does not take precedence over a column-level GRANT.
Row-Level Security and Data Masking for Privacy
Implementing Row-Level Security
Row-Level Security (RLS) enables the ability to use user execution context to control access to rows in a database table . We implement RLS to ensure that users can only see records that pertain to them, providing ‘record level’ security without requiring significant changes to applications.
The business logic is encapsulated within table-valued functions controlled by a security policy that toggles the RLS functionality on and off . The security policy controls the FILTER and BLOCK predicates that are bound to the tables RLS operates against. We recommend using RLS together with either Always Encrypted or Dynamic Data Masking to maximize the security posture of your organization.
Dynamic Data Masking Configuration
We configure Dynamic Data Masking to obscure sensitive data from non-privileged accounts, improving data security and compliance. Rather than showing credit card numbers, passwords, or personal identifiers in cleartext, we define masking rules at the column level so that specific users see only masked values while others with elevated permissions see the actual data.
Dynamic Data Masking is particularly effective for protecting personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, health information, and authentication credentials. We help organizations identify sensitive fields including email addresses, phone numbers, national identifiers such as SSN, credit card numbers, and passwords or security answers.
For lower environments where developers and testers often need realistic data, dynamic masking provides a systematic way to ensure personal information is never exposed. This approach helps maintain privacy protections throughout the data lifecycle while enabling development and testing workflows.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy
GDPR and CCPA Compliance
We ensure that SQL Server implementations align with basic data protection principles under GDPR and CCPA, allowing only correctly authorized users to see sensitive data in full view while other users receive masked or partial values. This decreases the possibility of unauthorized disclosure of personal information.
Well-documented masking rules and role-based permissions support the accountability principle of GDPR and the transparency requirements of CCPA. Auditors can easily verify that your organization has technical measures to safeguard personal information, helping demonstrate compliance and due diligence.
HIPAA and PCI-DSS Requirements
We help organizations implement SQL Server Dynamic Data Masking to ensure compliance with HIPAA for healthcare data and PCI-DSS for payment card information. These regulations require robust protection mechanisms for sensitive data, and we ensure that your SQL Server environment meets these requirements through comprehensive encryption, masking, and access control measures.
Auditing and Monitoring for Threat Detection
SQL Server Audit Implementation
We implement SQL Server Audit to provide a powerful framework for tracking database activities, allowing organizations to maintain a comprehensive record of user actions. By capturing and storing audit logs, organizations can analyze past events, identify patterns, and reinforce security measures.
We recommend creating audit policies at either the server or database level, with server policies applying to all existing and newly created databases on the server . For simplicity, we enable server-level auditing and allow database-level auditing to inherit the server-level property for all databases. We audit tables and columns with sensitive data that have security measures applied, as if a table or column is important enough to need protection by a security capability, it is important enough to audit.
Advanced Threat Protection Deployment
We deploy Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) to offer real-time monitoring and alerts for potential security threats. By analyzing database activities and identifying suspicious behavior, ATP enables organizations to respond swiftly to potential attacks, minimizing damage and ensuring data integrity.
The implementation of machine learning and artificial intelligence in ATP systems has revolutionized threat detection. These technologies enable ATP systems to learn from past incidents, improving the ability to identify and respond to new threats. We help organizations leverage AI and machine learning to enhance threat detection capabilities, ensuring that potential attacks are identified and addressed before causing significant damage.
Database Hardening and Surface Area Reduction
Surface Area Configuration
We implement surface area configuration to enable only the features required by your environment, minimizing the number of features that can be attacked by malicious users . We disable unused features or services such as SQL Mail and xp_cmdshell to reduce potential attack vectors.
We strongly advise against using xp_cmdshell on any SQL Server environment due to the risks it can introduce . Instead, we recommend SQLCLR or other alternatives that provide similar functionality without the associated security risks.
Network Security and Patch Management
We configure firewalls, disable unused protocols, and implement encrypted connections using SSL/TLS. We ensure that SQL Server and the host operating system are regularly updated to mitigate known vulnerabilities through comprehensive patch management.
We implement backup protection measures ensuring that backups are encrypted, stored securely, and tested regularly. This protects your data not only in production environments but also across backup and recovery scenarios.
Protecting Against Common SQL Server Threats
SQL Injection Prevention
We help organizations protect against SQL injection attacks, where malicious code is inserted into strings that are passed to SQL Server for execution . We implement several measures including reviewing any SQL process that constructs SQL statements for injection vulnerabilities, constructing dynamically generated SQL statements in a parameterized manner, and reviewing all code that calls EXECUTE, EXEC, or sp_executesql.
We disallow input characters that can be exploited including semicolons as query delimiters, single quotes as character data string delimiters, and comment delimiters . We always validate user inputs and scrub error outputs from being spilled and exposed to attackers.
Ransomware and Brute Force Protection
We implement measures to protect against ransomware attacks, which use malware to encrypt data and files, preventing access to important content . We use firewalls and lock down ports, ensure the latest operating system and application security updates are applied, implement group managed service accounts, and limit access to virtual machines.
We protect against brute force attacks where attackers attempt to authenticate with multiple passwords on different accounts . We create unique local administrator accounts that are not named Administrator, use complex strong passwords for all accounts, and regularly update passwords while enforcing Active Directory policies.
Secure Development Practices
Code Reviews and Vulnerability Assessments
We conduct regular code reviews and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security flaws in SQL Server applications. By involving security experts in the development process, organizations can ensure that applications adhere to best practices and remain resilient against emerging threats.
We use SQL vulnerability assessment tools in SSMS to discover, track, and remediate potential database vulnerabilities . We also implement SQL Data Discovery and Classification to discover, classify, label, and report on the sensitivity level of data.
DevSecOps Integration
We integrate security into the DevOps process through DevSecOps practices, ensuring that security is considered at every stage of the development lifecycle. We implement automated security testing and continuous integration/continuous deployment pipelines that provide real-time feedback on security issues.
Partner with MinervaDB for SQL Server Security Excellence
At MinervaDB, we bring deep expertise in database security, data privacy, and compliance to every engagement. We understand that SQL Server security requires a multifaceted approach, combining robust authentication, encryption, auditing, and secure development practices. By implementing these best practices, organizations can protect databases from sophisticated threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
We help organizations navigate the increasingly complex digital landscape by staying informed and proactive in database security. We provide comprehensive SQL Server security assessments, implementation services, and ongoing managed security operations to ensure your data assets remain protected against evolving cyber threats.
Contact MinervaDB today to discuss how we can strengthen your SQL Server security posture and protect your most valuable business asset—your data.