MongoDB Wire Protocol: Structure, Evolution, and Advantages
The MongoDB Wire Protocol serves as the fundamental communication backbone between MongoDB clients and servers, enabling seamless data exchange across distributed database systems. This simple socket-based, request-response style protocol allows clients to communicate with database servers through regular TCP/IP sockets, making it both efficient and widely compatible with existing network infrastructure.
Understanding the MongoDB Wire Protocol is crucial for developers, database administrators, and system architects who work with MongoDB deployments. This protocol not only defines how data flows between applications and databases but also influences performance, scalability, and the overall user experience of MongoDB-based systems.
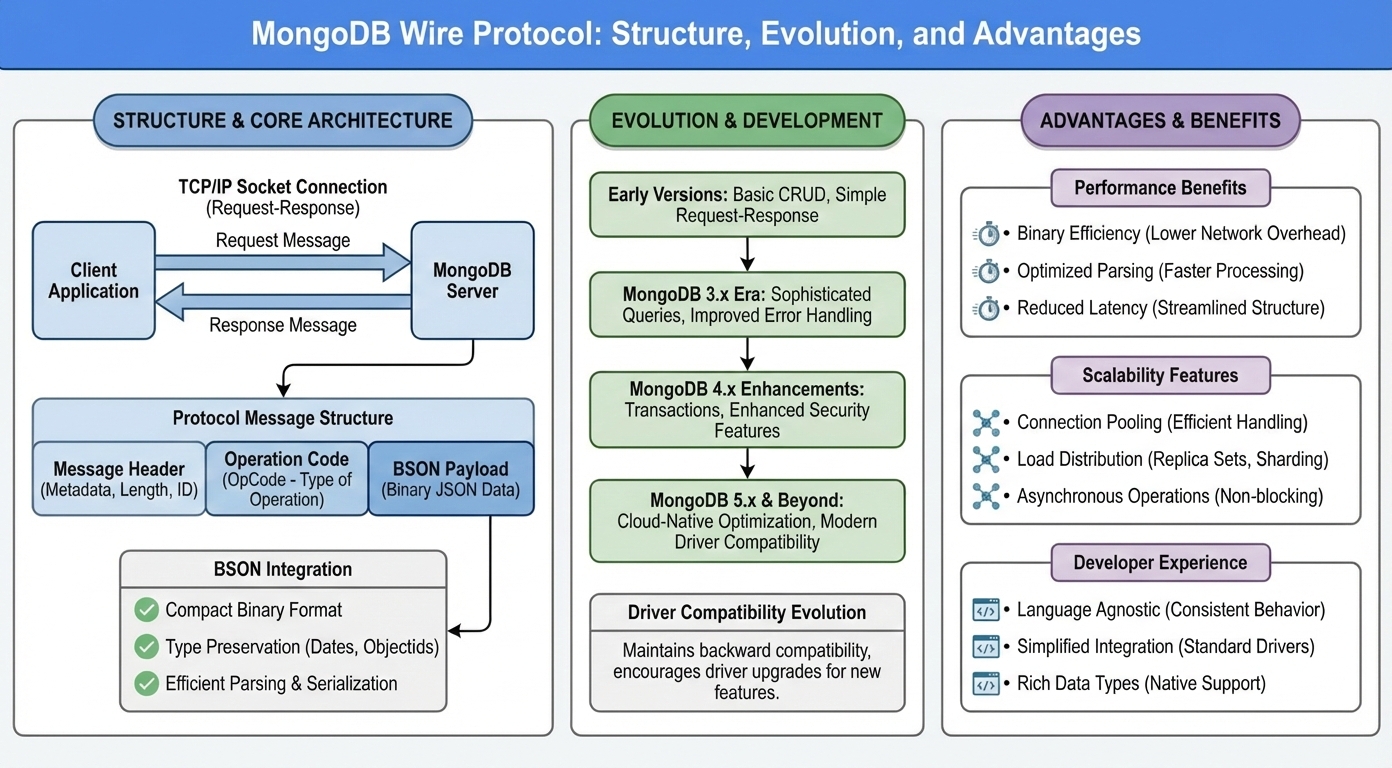
Structure of the MongoDB Wire Protocol
Core Architecture
The MongoDB Wire Protocol operates on a straightforward request-response modelthat prioritizes simplicity and efficiency. At its foundation, the protocol uses TCP/IP sockets for reliable communication, ensuring that messages are delivered in order and without corruption.
The protocol structure includes several key components:
- Message Headers: Each message contains metadata about the operation type, message length, and request identifiers
- Operation Codes: Specific codes that define the type of database operation being performed
- BSON Payload: The actual data being transmitted, encoded in Binary JSON format
- Response Handling: Structured responses that include status codes and result data
BSON Integration
One of the most significant aspects of the MongoDB Wire Protocol is its deep integration with BSON (Binary JSON). Unlike traditional text-based protocols, MongoDB uses BSON throughout its wire protocol implementation, providing several advantages:
- Compact Data Representation: BSON’s binary format reduces message size compared to plain JSON
- Type Preservation: Native support for MongoDB data types including dates, ObjectIds, and binary data
- Efficient Parsing: Binary format allows for faster serialization and deserialization
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Consistent data representation across different programming languages and platforms
Message Types and Operations
The protocol supports various message types that correspond to different database operations:
- Query Operations: For retrieving documents from collections
- Insert Operations: For adding new documents to the database
- Update Operations: For modifying existing documents
- Delete Operations: For removing documents from collections
- Administrative Commands: For database management and configuration tasks
Evolution of the MongoDB Wire Protocol
Historical Development
The MongoDB Wire Protocol has undergone significant evolution since MongoDB’s inception, adapting to meet the growing demands of modern applications and distributed systems. The protocol’s development has been driven by the need for improved performance, enhanced security, and better scalability.
Version-Specific Improvements
Throughout MongoDB’s version history, the wire protocol has incorporated numerous enhancements:
Early Versions: The initial protocol focused on basic CRUD operations with simple request-response patterns.
MongoDB 3.x Era: Introduction of more sophisticated query operations and improved error handling mechanisms.
MongoDB 4.x Enhancements: Added support for transactions and enhanced security features within the protocol layer.
MongoDB 5.x and Beyond: Continued optimization for cloud-native deployments and improved compatibility with modern driver implementations.
Driver Compatibility Evolution
As the protocol evolved, MongoDB has maintained backward compatibility while encouraging developers to upgrade to newer driver versions. This approach ensures that existing applications continue to function while providing access to new features and performance improvements.
Advantages of the MongoDB Wire Protocol
Performance Benefits
The MongoDB Wire Protocol offers several performance advantages that make it particularly well-suited for modern database applications:
- Binary Efficiency: The use of BSON reduces network overhead compared to text-based protocols
- Optimized Parsing: Binary format enables faster data processing on both client and server sides
- Reduced Latency: Streamlined message structure minimizes communication delays
- Efficient Memory Usage: Compact data representation reduces memory consumption during data transfer
Scalability Features
The protocol’s design inherently supports scalable database architectures:
- Connection Pooling: Efficient handling of multiple concurrent connections
- Load Distribution: Support for replica sets and sharded cluster communications
- Asynchronous Operations: Non-blocking communication patterns for improved throughput
- Resource Optimization: Minimal protocol overhead allows for higher connection density
Developer Experience
From a development perspective, the MongoDB Wire Protocol provides significant advantages:
- Language Agnostic: Consistent behavior across different programming languages and drivers
- Simplified Integration: Standard drivers handle protocol complexity, allowing developers to focus on application logic
- Rich Data Types: Native support for complex data structures without serialization overhead
- Error Handling: Comprehensive error reporting and status codes for robust application development
Security and Reliability
The protocol incorporates several features that enhance security and reliability:
- Authentication Integration: Built-in support for various authentication mechanisms
- Encryption Support: Compatibility with TLS/SSL for secure data transmission
- Connection Management: Robust handling of connection failures and recovery scenarios
- Data Integrity: Checksums and validation mechanisms to ensure data accuracy
Practical Implementation
Working with MongoDB Drivers
In practice, developers rarely interact directly with the MongoDB Wire Protocol. Instead, they use official MongoDB drivers that abstract the protocol complexity while providing language-specific APIs. Here’s how the protocol works behind the scenes:
// JavaScript example using MongoDB Node.js driver
const { MongoClient } = require('mongodb');
async function connectAndQuery() {
// Driver handles wire protocol communication
const client = new MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017');
await client.connect();
// This query operation uses the wire protocol internally
const database = client.db('myapp');
const collection = database.collection('users');
const result = await collection.findOne({ email: 'user@example.com' });
await client.close();
return result;
}
Protocol Flow Example
When the above code executes, the following wire protocol communication occurs:
- Connection Establishment: TCP socket connection to MongoDB server
- Authentication: Protocol-level authentication handshake
- Query Message: BSON-encoded query sent via wire protocol
- Response Processing: Server response parsed from BSON format
- Connection Management: Efficient connection reuse or cleanup
Custom Protocol Implementations
For specialized use cases, developers can implement custom wire protocol handlers:
# Python conceptual example for custom protocol handling
import socket
import bson
class MongoWireProtocol:
def __init__(self, host, port):
self.socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.socket.connect((host, port))
def send_query(self, database, collection, query):
# Construct wire protocol message
message = self._build_query_message(database, collection, query)
self.socket.send(message)
# Receive and parse response
response = self.socket.recv(4096)
return self._parse_response(response)
def _build_query_message(self, database, collection, query):
# Implementation would construct proper BSON message
# following MongoDB wire protocol specification
pass
def _parse_response(self, response):
# Parse BSON response according to wire protocol format
pass
Integration with Modern Architectures
The MongoDB Wire Protocol seamlessly integrates with contemporary application architectures:
- Microservices: Each service can maintain independent database connections
- Container Deployments: Protocol works efficiently in containerized environments
- Cloud-Native Applications: Optimized for distributed cloud deployments
- API Gateways: Compatible with various API management and routing solutions
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Understanding the wire protocol helps in performance optimization:
- Connection Pooling: Configure appropriate pool sizes based on protocol behavior
- Query Optimization: Structure queries to minimize protocol overhead
- Network Tuning: Optimize network settings for protocol efficiency
- Monitoring Tools: Use protocol-aware monitoring for better insights
Conclusion
The MongoDB Wire Protocol represents a sophisticated yet accessible approach to database communication that has evolved to meet the demands of modern applications. Its binary efficiency, BSON integration, and scalable architecture make it an excellent choice for applications requiring high performance and reliability.
By understanding the protocol’s structure, evolution, and advantages, developers and administrators can make informed decisions about MongoDB deployments and optimize their applications for better performance. The protocol’s continued evolution ensures that MongoDB remains competitive in the rapidly changing landscape of database technologies.
Whether you’re building a simple web application or a complex distributed system, the MongoDB Wire Protocol provides the robust foundation necessary for reliable, efficient database communication. Its balance of simplicity and power continues to make MongoDB an attractive choice for developers worldwide.
Further Reading
- PostgreSQL 16 for DBAs: Essential Features and Practical Implementation Guide
- PostgreSQL DELETE vs TRUNCATE: A Complete Guide to Data Removal Commands
- Mastering Google Cloud Dataflow and Apache Airflow Integration: A Comprehensive Guide for Data Engineers
- Mastering PostgreSQL Replication: A Complete Guide for Database Professionals
- Comprehensive Guide to MySQL to Amazon Redshift Data Replication Using Tungsten Replicator
- Eliminating Expensive JOINs in ClickHouse


