MongoDB Aggregation Framework: Comprehensive Guide for Modern Web Development
The MongoDB Aggregation Framework represents a paradigm shift in how developers approach data processing and analysis within NoSQL database environments. As organizations increasingly rely on complex data transformations and real-time analytics, the aggregation framework has emerged as a cornerstone technology for building sophisticated web applications that demand high-performance data manipulation capabilities.
This comprehensive framework provides developers with a powerful, flexible, and efficient mechanism for processing documents within MongoDB collections, enabling complex data transformations, statistical computations, and analytical operations that would traditionally require multiple database queries or external processing systems. The aggregation framework’s pipeline-based architecture allows for the creation of sophisticated data processing workflows that can handle everything from simple filtering operations to complex multi-stage transformations involving joins, groupings, and statistical calculations.
Framework Architecture and Core Concepts
Pipeline-Based Processing Model
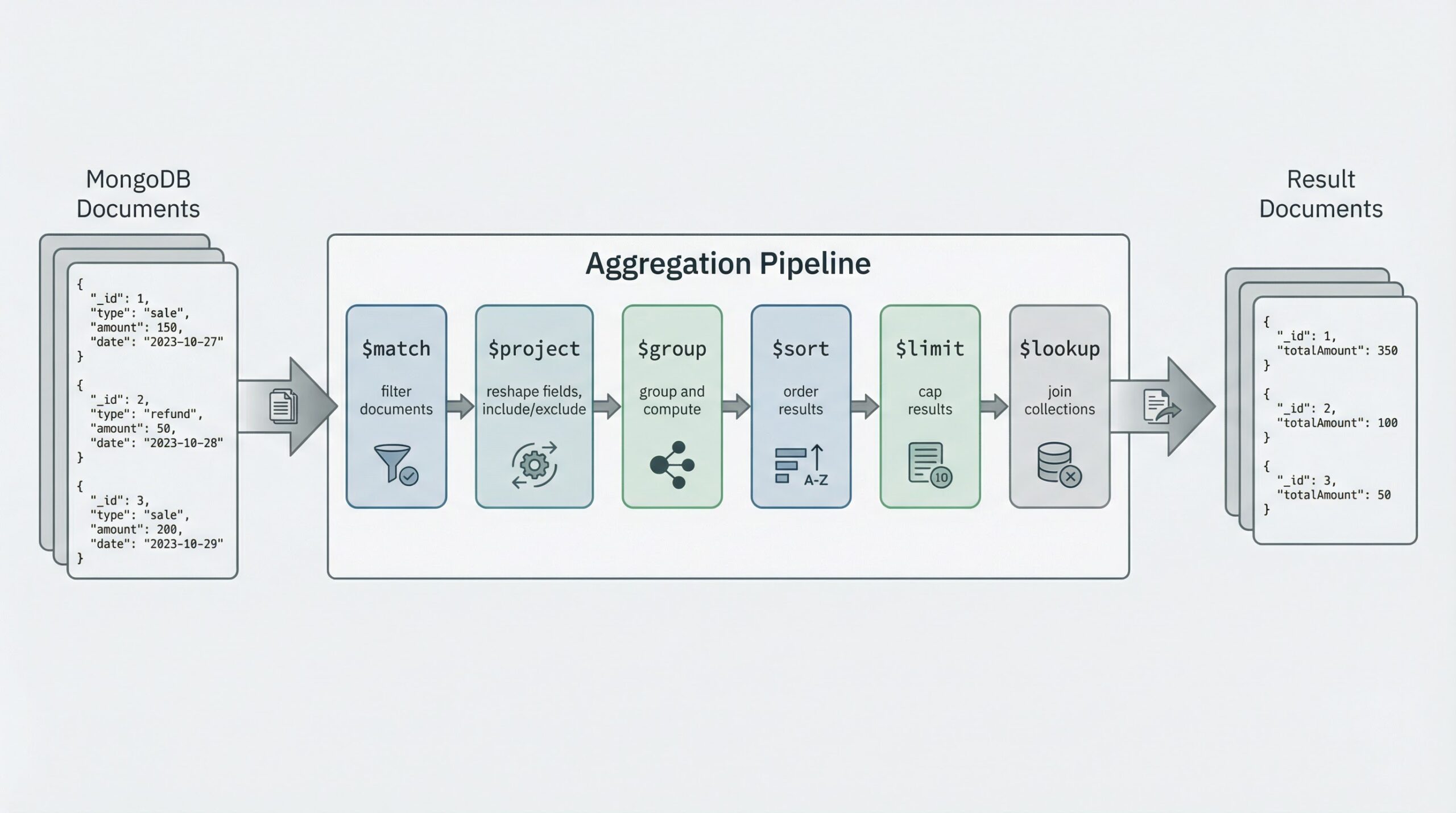
The MongoDB Aggregation Framework operates on a pipeline-based processing model, where data flows through a series of stages, each performing specific transformations or operations on the document stream. This architectural approach provides several distinct advantages over traditional query mechanisms, including improved performance through optimized execution plans, enhanced readability through declarative syntax, and increased flexibility through modular stage composition.
Each stage in the aggregation pipeline receives documents from the previous stage, processes them according to its specific operation, and passes the results to the subsequent stage. This sequential processing model enables developers to build complex data transformations by combining simple, well-defined operations, resulting in maintainable and efficient code that can be easily understood and modified.
Stage-Based Operations
The framework encompasses numerous stage types, each designed to address specific data processing requirements. The $match stage provides document filtering capabilities equivalent to traditional query operations, while the $group stage enables sophisticated aggregation operations including sum, average, count, and custom accumulator functions. The $project stage allows for document reshaping and field manipulation, enabling developers to control the structure and content of output documents.
Advanced stages such as $lookup provide join-like functionality for combining data from multiple collections, while $unwind enables array deconstruction for processing embedded document arrays. The $sort and $limit stages provide result ordering and pagination capabilities, essential for web application interfaces that require controlled data presentation.
Key Features and Capabilities
Advanced Data Transformation
The aggregation framework excels in performing complex data transformations that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through traditional query operations. The framework supports sophisticated mathematical operations, string manipulations, date calculations, and conditional logic, enabling developers to implement business rules and data processing logic directly within the database layer.
Expression operators provide extensive functionality for field manipulation, including arithmetic operations, string concatenation and parsing, date formatting and extraction, and conditional expressions. These capabilities enable developers to perform data cleansing, normalization, and enrichment operations as part of the aggregation pipeline, reducing the need for application-level data processing.
Performance Optimization Features
MongoDB’s aggregation framework incorporates numerous performance optimization features designed to maximize query execution efficiency. The query optimizer automatically analyzes aggregation pipelines and applies various optimization techniques, including stage reordering, index utilization, and predicate pushdown, to minimize execution time and resource consumption.
Index utilization represents a critical performance consideration, as properly designed indexes can dramatically improve aggregation performance, particularly for $match and $sort operations. The framework’s ability to leverage compound indexes and partial indexes enables developers to optimize performance for specific aggregation patterns commonly used in their applications.
Scalability and Distribution
The framework’s design inherently supports MongoDB’s distributed architecture, enabling aggregation operations to execute efficiently across sharded clusters. The aggregation pipeline automatically distributes processing across multiple shards when possible, leveraging parallel processing capabilities to handle large-scale data processing requirements.
Sharding considerations become particularly important for aggregation operations that require data from multiple shards, such as global grouping operations or cross-shard joins. The framework’s intelligent query planning ensures optimal distribution of processing load while minimizing network traffic between shards.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Pipeline Design Principles
Effective aggregation pipeline design requires careful consideration of stage ordering and operation efficiency. Placing $match stages early in the pipeline reduces the number of documents processed by subsequent stages, improving overall performance. Similarly, $project stages should be positioned strategically to eliminate unnecessary fields before expensive operations such as $group or $lookup.
Pipeline readability and maintainability represent crucial considerations for long-term application success. Developers should adopt consistent naming conventions, provide comprehensive documentation for complex pipelines, and consider breaking extremely complex aggregations into multiple smaller operations when appropriate.
Error Handling and Validation
Robust aggregation implementations require comprehensive error handling and data validation strategies. The framework provides various mechanisms for handling missing fields, null values, and data type inconsistencies that commonly occur in real-world datasets. Conditional expressions and error handling operators enable developers to implement graceful degradation strategies that maintain application functionality even when encountering unexpected data conditions.
Input validation becomes particularly important when aggregation pipelines accept dynamic parameters from web application interfaces. Proper sanitization and validation of user inputs prevent injection attacks and ensure pipeline stability under various operating conditions.
Memory Management Considerations
Aggregation operations can consume significant memory resources, particularly when processing large datasets or performing memory-intensive operations such as sorting or grouping. Understanding memory limitations and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies ensures stable application performance under varying load conditions.
The framework provides several mechanisms for managing memory consumption, including the allowDiskUse option for operations that exceed memory limits, and streaming processing capabilities that enable handling of datasets larger than available memory. Developers should carefully monitor memory usage patterns and implement appropriate resource management strategies based on their specific application requirements.
Real-World Use Cases and Applications
Business Intelligence and Analytics
The aggregation framework serves as a foundation for building sophisticated business intelligence and analytics applications. Complex reporting requirements, including multi-dimensional analysis, trend calculations, and statistical computations, can be efficiently implemented using aggregation pipelines that process data directly within the database layer.
Real-time dashboard applications benefit significantly from the framework’s ability to perform complex calculations and data transformations with minimal latency. By leveraging MongoDB’s aggregation capabilities, developers can create responsive analytics interfaces that provide users with up-to-date insights without requiring separate data processing systems.
Content Management and Personalization
Modern web applications increasingly rely on personalized content delivery based on user behavior, preferences, and contextual factors. The aggregation framework enables sophisticated content recommendation algorithms that analyze user interactions, content relationships, and temporal patterns to deliver relevant, personalized experiences.
Content aggregation and curation workflows benefit from the framework’s ability to combine data from multiple sources, apply complex filtering and ranking algorithms, and generate customized content feeds tailored to individual user preferences.
E-commerce and Transaction Processing
E-commerce applications require complex data processing capabilities for inventory management, pricing calculations, order processing, and customer analytics. The aggregation framework provides the necessary tools for implementing sophisticated business logic directly within the database layer, reducing application complexity and improving performance.
Transaction analysis and fraud detection systems leverage the framework’s statistical and pattern recognition capabilities to identify suspicious activities and implement risk management strategies. Real-time processing capabilities enable immediate response to potential security threats while maintaining smooth user experiences for legitimate transactions.
Performance Optimization and Monitoring
Index Strategy Development
Effective index strategies represent the foundation of high-performance aggregation operations. Developers must carefully analyze aggregation patterns and design indexes that support the most common and performance-critical operations. Compound indexes that support multiple pipeline stages can significantly improve overall performance, while partial indexes reduce storage overhead for specialized use cases.
Index monitoring and maintenance require ongoing attention to ensure optimal performance as data volumes and access patterns evolve. Regular analysis of query execution statistics and index utilization metrics enables proactive optimization and prevents performance degradation over time.
Query Performance Analysis
MongoDB provides comprehensive tools for analyzing aggregation performance, including detailed execution statistics, stage-by-stage timing information, and resource utilization metrics. Regular performance analysis enables developers to identify bottlenecks, optimize pipeline design, and ensure consistent application performance under varying load conditions.
Profiling and monitoring strategies should encompass both individual query performance and overall system behavior under realistic load conditions. Load testing with representative data volumes and access patterns provides valuable insights into scalability characteristics and potential performance limitations.
Future Considerations and Evolution
Emerging Capabilities
The MongoDB aggregation framework continues to evolve with new features and capabilities that address emerging application requirements. Recent additions include enhanced text processing capabilities, improved geospatial operations, and expanded statistical functions that enable more sophisticated analytical applications.
Machine learning integration represents an exciting frontier for aggregation framework development, with potential applications including real-time model scoring, feature engineering, and automated pattern recognition directly within the database layer.
Integration with Modern Development Practices
Contemporary web development practices emphasize microservices architectures, containerized deployments, and cloud-native design patterns. The aggregation framework’s flexibility and performance characteristics make it well-suited for these modern architectural approaches, enabling developers to build scalable, maintainable applications that leverage the full capabilities of distributed computing environments.
Conclusion
The MongoDB Aggregation Framework represents a mature, powerful solution for complex data processing requirements in modern web applications. Its pipeline-based architecture, comprehensive feature set, and performance optimization capabilities enable developers to build sophisticated applications that efficiently handle complex data transformations and analytical operations.
Success with the aggregation framework requires careful attention to design principles, performance optimization strategies, and ongoing monitoring practices. By leveraging the framework’s capabilities effectively, development teams can create applications that deliver exceptional performance, scalability, and functionality while maintaining code clarity and maintainability.
As data processing requirements continue to evolve and grow in complexity, the MongoDB Aggregation Framework provides a solid foundation for building next-generation web applications that can adapt to changing business needs while delivering consistent, high-performance user experiences. The framework’s continued evolution and enhancement ensure that it will remain a valuable tool for developers building data-intensive applications in the years to come.