Cloud DBA Services by MinervaDB
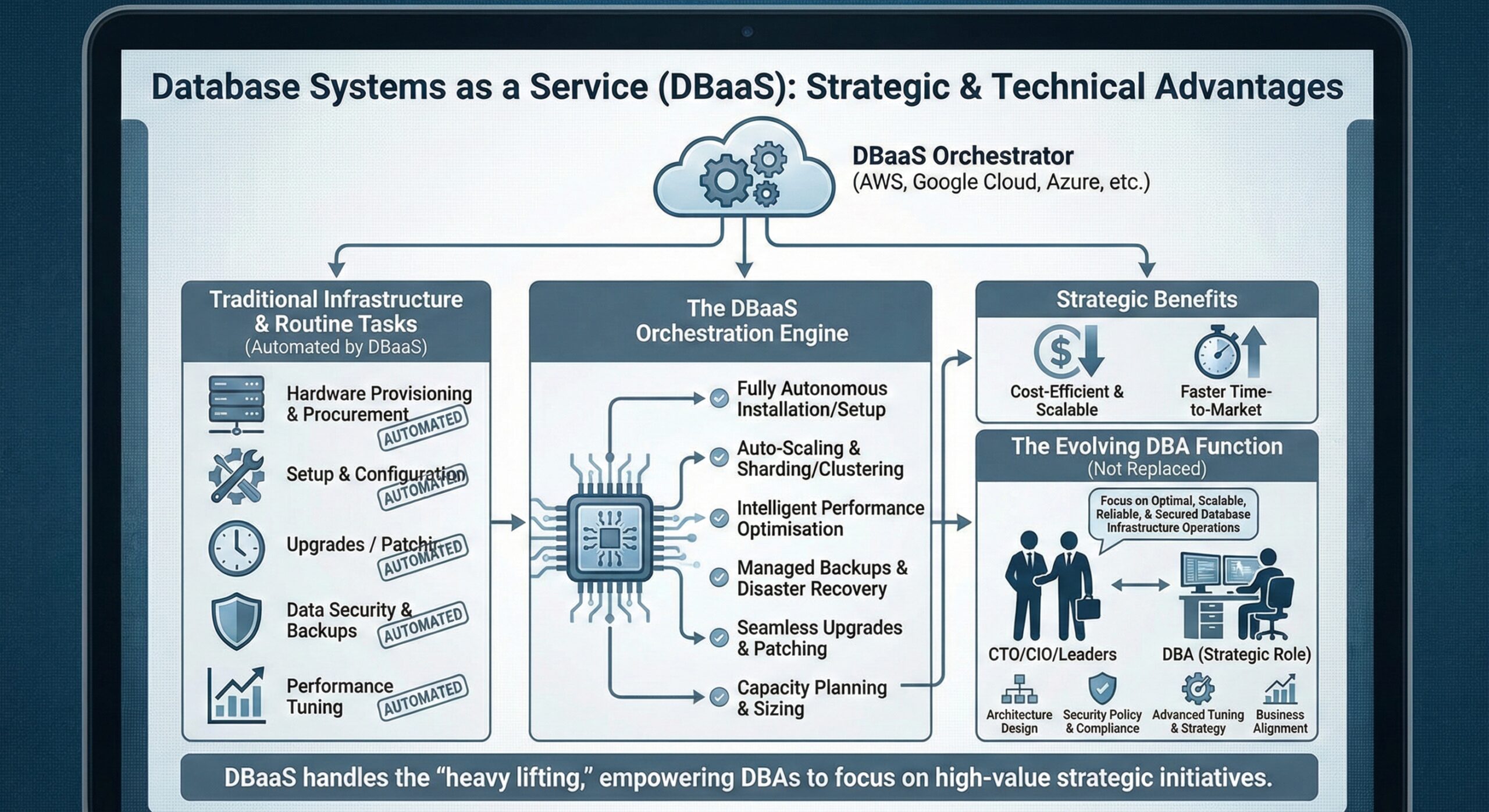
☛ Why Database Systems as a Service (DBaaS) is technically and strategically so compelling for building Database Infrastructure for Performance and Scalability?
-
Cost-efficient and scalable
-
Time-to-Market benefits
-
Database Infrastructure Maintenance Operations Routine Tasks will be automated:
-
Setup and configuration
-
Fully autonomous performance tuning/optimisation
-
Backup and DR
-
Capacity Planning and Sizing
-
Scale-out / Sharding / Clustering Solution
-
Upgrades / Patching
-
☛ How MinervaDB can help you with Cloud DBA Services for building optimal, scalable and cost-efficient Database Systems as a Service (DBaaS) on AWS(Amazon Cloud), GCP(Google Cloud)and Microsoft Azure
-
Database Architecture (Logical and Physical Schema) Design and Engineering Services
-
Optimal SQL Engineering Services
-
Optimal Indexing
-
SQL Tuning Services
-
Database Application Design/Engineering Performance Audit and Recommendations
-
Architecting and Engineering Secured Database Infrastructure:
-
GDPR: General Data Protection Directive
-
PCI DSS: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
-
HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
-
HITECH: Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act
-
Data Protection Act: United Kingdom
-
SOX: Sarbanes Oxley
-
FERPA: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act
-
And many more
-
☛ The Costly Impact of Poorly Performing PostgreSQL Queries in Amazon RDS and Aurora: A Data-Driven Analysis
Poorly performing PostgreSQL queries can significantly impact operational costs and complexities in Amazon RDS and Aurora, often incurring unnecessary expenses. Here’s an exploration of this issue with added statistics and practical, real-life data set examples:
-
Example: Consider an e-commerce application hosted on Amazon RDS that runs complex queries to retrieve product information. These queries may require extensive CPU and memory resources if they are not well-optimised.
-
Impact: High CPU and memory usage can lead to the need for larger RDS instances, resulting in increased operational costs.
-
Statistics: On average, poorly optimized queries can cause CPU usage to spike by 40% and memory usage to increase by 60%.
-
Example: In an Amazon Aurora database used for a content management system, poorly optimized queries for retrieving articles can lead to slow response times.
-
Impact: Slow queries can affect user experience, leading to decreased customer satisfaction and potentially lost revenue. It may also require read replicas or additional database instances to handle the load.
-
Statistics: Inefficient queries can increase query response times by up to 200%, resulting in a 30% decrease in user engagement.
-
Example: If you have an application that generates excessive temporary tables due to suboptimal queries, it can lead to a significant increase in storage usage.
-
Impact: You might need to allocate more storage capacity for your RDS or Aurora instances, incurring additional storage costs.
-
Statistics: Inefficient queries can inflate storage usage by 50%, causing a corresponding rise in storage expenses.
-
Example: Suppose you have a large dataset in Amazon RDS for user analytics, and queries for aggregating data are not optimized. To improve performance, you may need to add more indexes or rewrite queries.
-
Impact: Database administrators and developers spend extra time on query optimization and indexing, adding to operational complexity.
-
Statistics: Query optimization and indexing efforts can consume 20-30% of a database team’s time, diverting resources from other critical tasks.
-
Example: An online gaming platform using Amazon RDS experiences high traffic during peak hours. Poorly performing queries can limit the scalability of the database.
-
Impact: You might need to horizontally scale (add more RDS or Aurora instances) to meet demand, increasing operational complexity and costs.
-
Statistics: Scalability constraints due to suboptimal queries can lead to a 40% increase in infrastructure costs during peak periods.
-
Example: If inefficient queries result in frequent updates or inserts, Amazon RDS and Aurora generate more transaction logs.
-
Impact: More frequent backups consume additional storage and can increase backup-related costs.
-
Statistics: Transaction logs generated by inefficient queries can inflate backup storage requirements by 25%.
-
Example: In a healthcare application, slow queries for retrieving patient records might impact compliance with response time requirements.
-
Impact: Failure to meet compliance requirements can result in fines and legal issues, adding to operational risks.
-
Statistics: Non-compliance due to slow queries can lead to an average fine of $50,000 per incident.
☛ Technology focus – Vendor-neutral and independent
| Category | Technology | Enterprise Ready | 24/7 Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Databases | PostgreSQL | ✓ | ✓ |
| MySQL | ✓ | ✓ | |
| MariaDB | |||
| SQL Server | ✓ | ✓ | |
| NoSQL Document | MongoDB | ✓ | ✓ |
| CouchDB | ✓ | ✓ | |
| NoSQL Key-Value | Redis | ✓ | ✓ |
| Valkey | ✓ | ✓ | |
| NoSQL Wide-Column | Cassandra | ✓ | ✓ |
| HBase | ✓ | ✓ | |
| NoSQL Graph | Neo4j | ✓ | ✓ |
| Analytics | ClickHouse | ✓ | ✓ |
| Trino | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Vertica | ✓ | ✓ | |
| GreenPlum | ✓ | ✓ | |
| NewSQL | CockroachDB | ✓ | ✓ |
| TiDB | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Vector Databases | Milvus | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pinecone | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Cloud Platforms | AWS RDS | ✓ | ✓ |
| Azure SQL | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Google Cloud SQL | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Google AlloyDB | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Amazon Aurora | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Snowflake | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Databricks | ✓ | ✓ | |
| BigQuery | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Redshift | ✓ | ✓ | |
| MySQL HeatWave | ✓ | ✓ |
☛ Remote DBA Plans for Database Systems as a Service(DBaaS)
We are transparent in sharing how we bill our customers for remote DBA services. There are absolutely no hidden costs attached; You will pay only what we have mentioned below. Our remote DBA plans are independent of how many database servers we are managing for you; The fixed-priced billing model gives you strong control over the budget you have for database infrastructure operations management.
| Remote DBA Plan | Rate ( plus GST / Goods and Services Tax where relevant ) |
|---|---|
| On-Demand Remote DBA (8 hours Remote DBA per month) | US $3,600 / month |
| Quarter DBA (40 hours of remote DBA services per month) | US $9,000 / month |
| Half DBA (80 hours of remote DBA services per month) | US $13,000 / month |
| Full DBA (160 hours of remote DBA services per month) | US $19,000 / month |
| The Ultimate DBA (Remote DBA services for 24*7*365) | US $75,000 / month |
★ We deliver Remote DBA Services for PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, MongoDB, ClickHouse, Trino, Cassandra, Redis, Valkey, Milvus and Cloud Database Infrastructure/DBaaS(Oracle MySQL HeatWave, Amazon RDS, AzureSQL, Redshift, Amazon Aurora, Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Databricks) addressing Performance, Scalability, High Availability, Data Reliability Engineering and Data Security.
★ We don’t bill you per instance; our remote DBA plans are not dependent on the number of Database Instances we manage for you!
☛ Further Reading:
